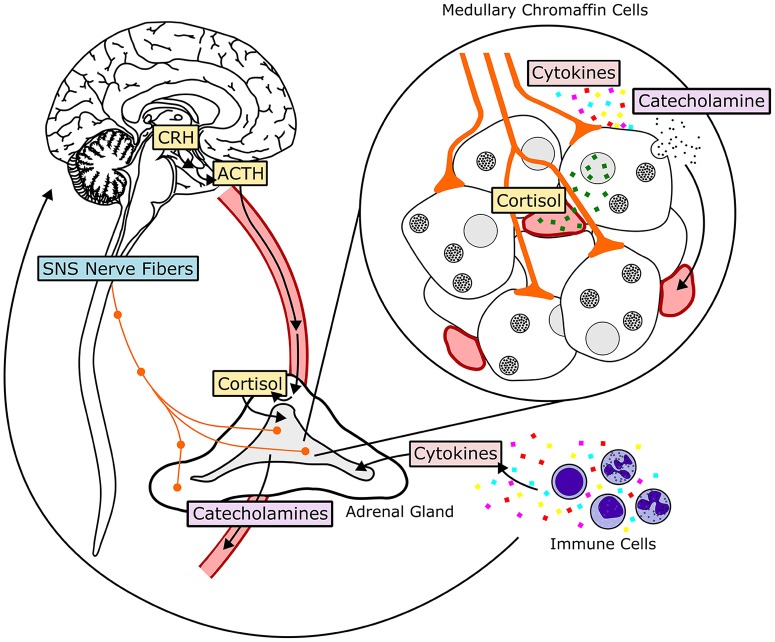
Figure 3.
Hormonal and neural mechanisms regulating adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. The HPA-axis, comprised of the hormones corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and cortisol, is shown in yellow. The SA-axis, comprised of afferent preganglionic sympathetic nervous system (SNS) fibers, is shown in blue. Green squares represent glucocorticoid (cortisol) produced in the adrenal cortex and traveling to the adrenal medulla through vasculature. Acetylcholine, pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating peptide, and other neurotransmitters are released from synaptic terminals. Cytokines, transported to the adrenal medulla or produced locally, influence adrenal chromaffin cell function and response to HPA- and SA-axis activation. Both glucocorticoids and sympathetic input stimulate release of catecholamines, primarily epinephrine, from chromaffin cells by exocytosis. Epinephrine then enters systemic circulation and travels to target tissues throughout the body.