Figure 2.
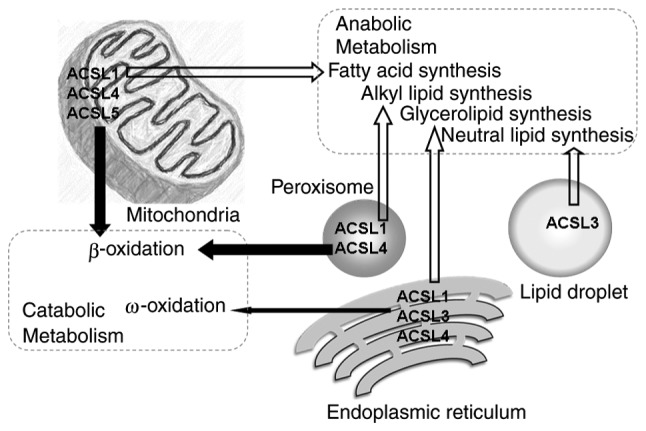
Subcullular localization and function of ACSL isoforms. ACSL members reside in different subcellular organelles to channel fatty acids into two distinct metabolic pathways. The white arrows refer to channeling to anabolic metabolism, while the black arrows refer to catabolic metabolism. ACSL, long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase.
