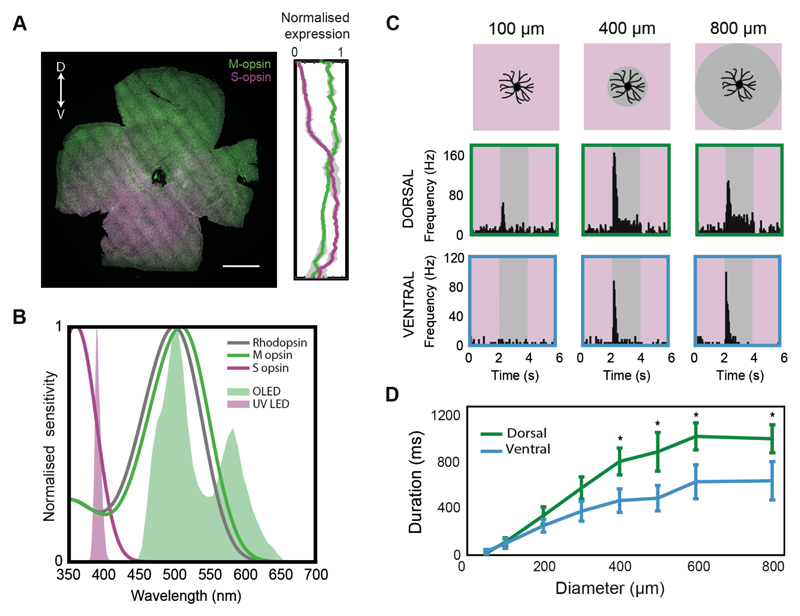
Figure 3. Differential cone activation cannot explain the different length responses in dorsal- and ventral-tOff-αRGCs.
(A) Left, an example of a retina immunostained for M (green) and S (magenta) opsin. Double-headed arrow indicates retinal orientation, D: dorsal, V: ventral, scale bar: 1000 μm. Right, Quantification of relative M and S opsin expression along the dorsal-ventral axis, averaged from three mice. (B) Graph showing the absorption spectrum for Rhodopsin, M and S opsin, and the light spectrum for the OLED (white light stimulus used in this study) and the UV LED (used exclusively for this figure). (C) PSTHs for example dorsal-tOff-αRGC (middle) and ventral-tOff-αRGC (bottom) when a UV light stimulus is used. Top line illustrates the corresponding spot stimuli. (D) Response duration as a function of spot size for dorsal- and ventral-tOff-αRGCs, when UV light stimulus is used. Error bars represent the mean ± s.e.m., n=12 cells from 6 retinas for dorsal, n=12 cells from 5 retinas for ventral, * P<0.05, according to Wilcoxon Rank Sum test.