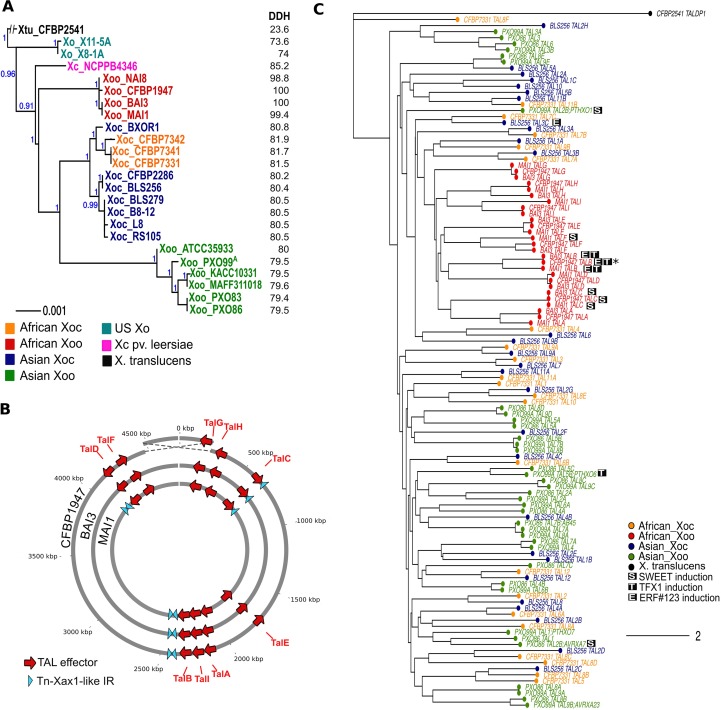
Fig 1. Genomes and TALomes of African Xoo compared with other X. oryzae strains.
A. MLSA-based phylogenetic tree of X. oryzae strains, built based on alignment of the amino acid sequences of 33 concatenated housekeeping genes using MUSCLE v.3.8.31 [66] and PhyML v. 3.1 [68]. Numbers in blue indicate branch support as calculated by approximate likelihood ratio tests (aLRT) in PhyML v. 3.1 [68]. The X. campestris pv. leersiae strain NCPPB4346 was included with the X. oryzae strains examined. X. translucens strain CFBP2541 was used as an out-group (left). Numbers in black indicate in silico DNA-DNA hybridization (DDH) as calculated using Genome-to-Genome Distance Calculator [45] with the X. oryzae pv. oryzae strain BAI3 as a reference. B. Circular representation of three African X. oryzae pv. oryzae strains showing positions of TAL effector genes and TnXax1-like inverted repeats. Features are not drawn to scale and position is approximate. Dashed lines highlight a 434kb inversion containing the replication origin in Xoo strain CFBP1947 in comparison to strains BAI3 and MAI1. C. Neighbour-joining tree built using the program DisTAL [47] based on alignments of repeat regions from TAL effectors from selected X. oryzae strains with fully sequenced TALomes. Strains used were (number of TAL effectors in parentheses): Xoc = BLS256 (28), CFBP7331 (22), Xoo = BAI3 (9), CFBP1947 (9), MAI1 (9), PXO83 (18), PXO86 (18) and PXO99A (18). Each tip represents a TAL effector. Tip colors indicate the pathovar and geographic group of the strain; TalDP1 from X. translucens CFBP2541 was used as outgroup (accession number WP 039006168.1). S, T and E indicate that the TAL effectors can induce OsSWEET11 or OsSWEET14, OsTFX1 or OsERF#123 respectively. Asterisks indicate instances where the induction of the corresponding target is hypothesized. Scale bar represents branch lengths as calculated by the nj function of the package ape [69] on a distance matrix of alignments generated by DisTAL [47].