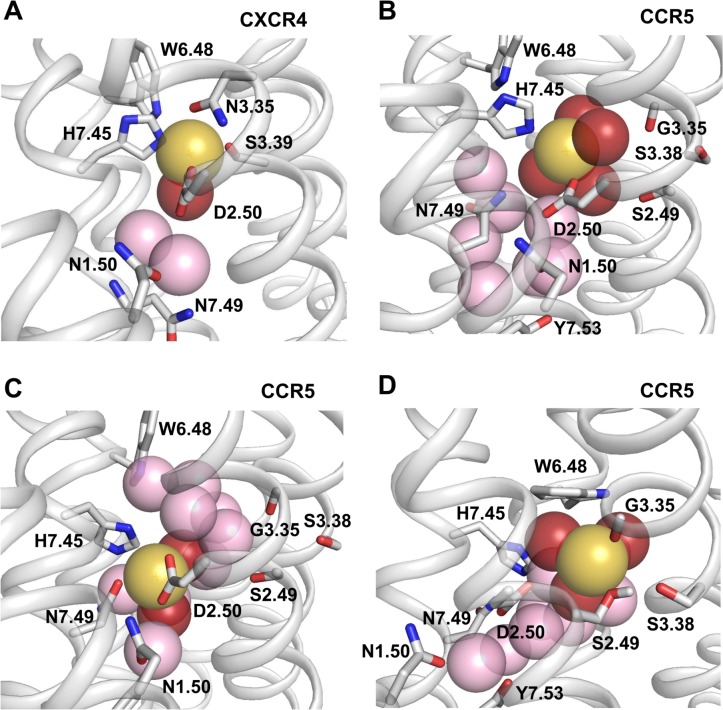
Fig 4. Representative snapshots of the sodium binding site in CXCR4 and CCR5.
In (A), the sodium ion bound to CXCR4 interacts with D2.50, N3.35, S3.39, H7.45, and a water molecule. In (B), the sodium ion bound to CCR5 interacts with D2.50, H7.45, and four water molecules. In (C), the sodium ion bound to CCR5 interacts with D2.50 (bivalent coordination), N7.49, and two water molecules. In (D), the sodium ion bound to CCR5 interacts with the carbonyl group of G3.35, the hydroxyl group of S2.49 and three water molecules. D2.50 is in the second coordination shell and interacts with the sodium ion through a water molecule. In the four plots, sodium is shown as a yellow sphere. Water molecules within the sodium binding pocket are shown as spheres. Those within 3 Å of the sodium ion are red, otherwise they are pink. Side chains interacting with the sodium ion or contributing to the sodium binding site are shown as sticks. For clarity purpose, hydrogen atoms are not shown except the hydrogen of the hydroxyl group of S2.49 in (D) which is H-bonded to S3.38.