Figure 2. A panel of kinase activity and activation biosensors.
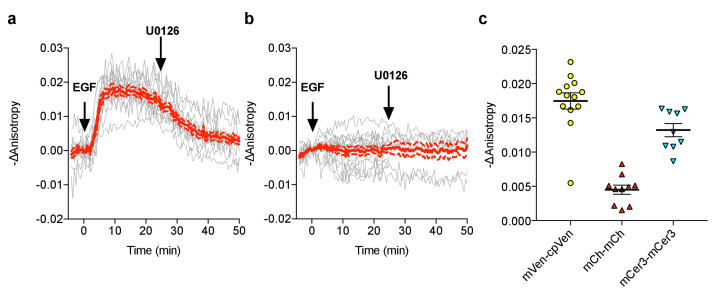
(a) Domain structure of FLARE-EKAR-EV (above). Time-course of mean fluorescence anisotropy of Venus-cp172Venus FLARE-EKAR-EV WT (blue, N = 13) and kinase-insensitive mutant (red, N = 16) expressed in HEK293T cell, with addition of 100 ng/mL EGF at t = 0 min and 20 μM U0126 at t = 25 min (left). Summary of anisotropy changes (upper right, two-tailed t-test, p<0.0001), calculated as the difference between the mean anisotropy from t = 10 min to t = 15 min and the mean anisotropy of the baseline before drug addition. The mean is shown, with the error reflecting the standard error of the mean. Representative anisotropy pseudocolor image before EGF stimulation (t = 0 min), after EGF stimulation (t = 25 min), and after inhibition of MEK with U0126 (t = 47.5 min) (lower right). (b) Domain structure of FLARE-CKAR (above). Time-course of fluorescence anisotropy of Venus-cp172Venus FLARE-CKAR WT (blue, N = 26) and kinase-insensitive mutant (red, N = 119) with addition of 100 ng/mL phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) at t = 0 min. Summary of response magnitudes (upper right, two-tailed t-test, p<0.0001), calculated as the difference between the mean anisotropy from t = 10 to t = 11.33 min and the mean anisotropy of the baseline before drug addition. The mean is shown, with the error reflecting the standard error of the mean. Representative anisotropy pseudocolor image before PMA addition (t = 0 min) and after PMA addition (t = 15 min). (c) Domain structure of FLARE-MLCK (top). Anisotropy time course of a representative REF52 cell expressing YFP-Venus FLARE-MLCK treated with 30 mM KCl at t = 0 (N = 13, blue), or vehicle control (N = 10). Summary of anisotropy changes, calculated as the mean difference between the anisotropy at t = 0.333 min and the anisotropy of the baseline, before KCl addition (upper right, two-tailed t-test, p<0.0001). Representative pseudocolor anisotropy images before and after KCl treatment (lower right). Dashed lines above and below time course traces reflect the standard error of the mean. FP, fluorescent protein; CaM BD, MLCK calmodulin-binding domain.
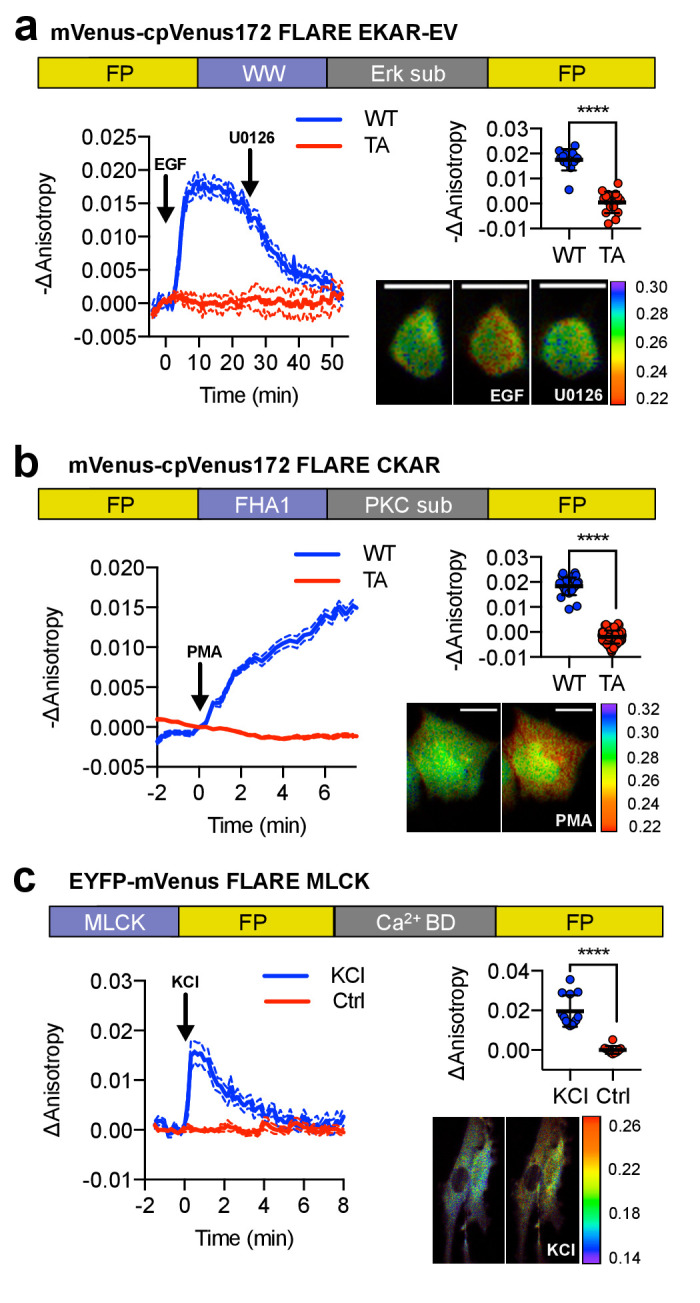
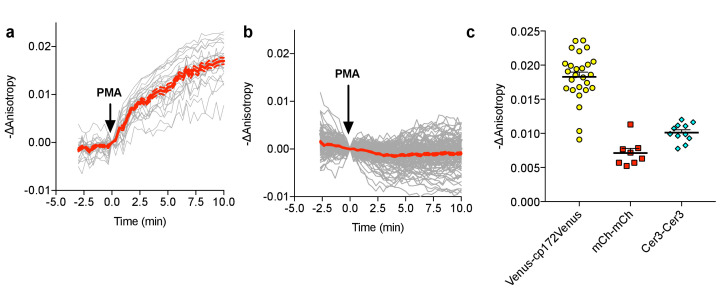
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. FLARE-EKAR characterization.
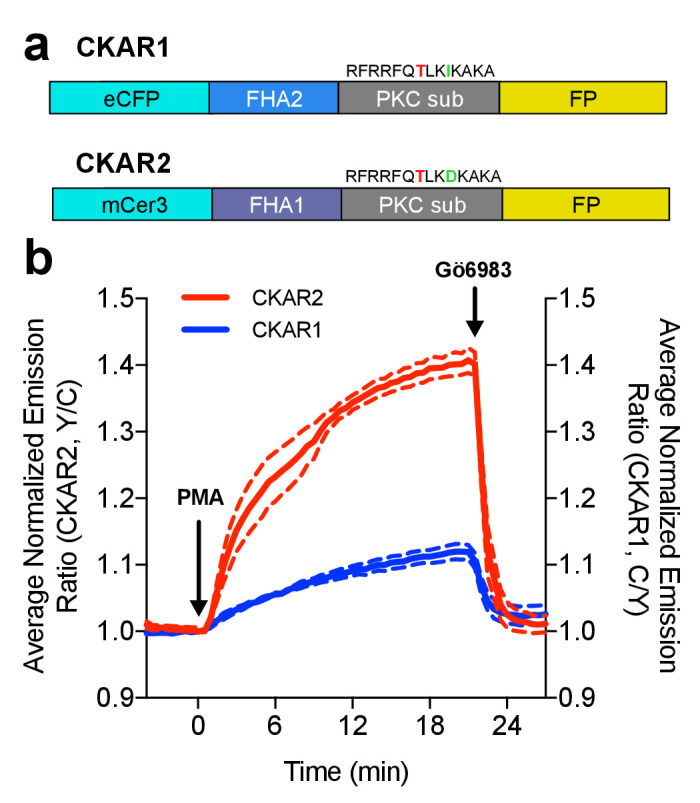
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Characterization of the CKAR2 hetero-FRET biosensor.