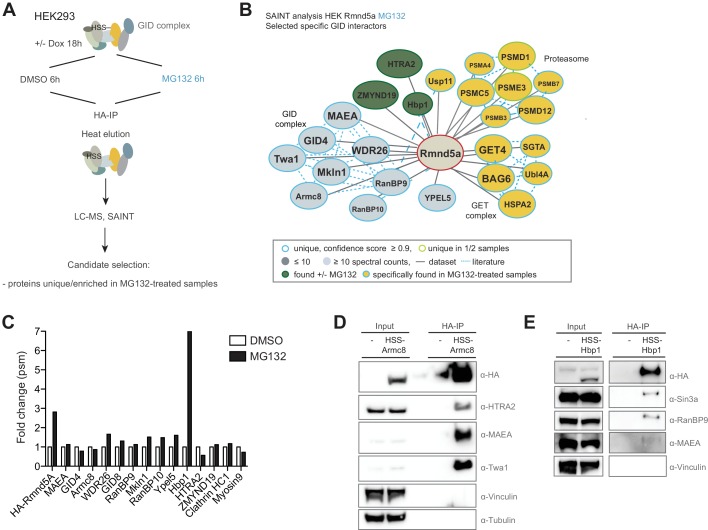
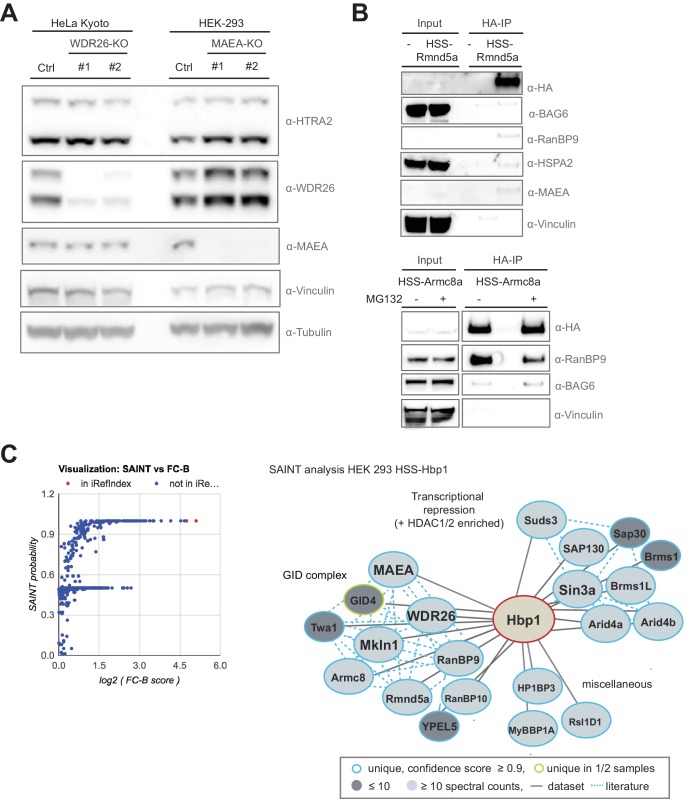
Figure 4. Semi-quantitative proteomics identifies novel stable and regulated GID-interacting proteins.
(A) Scheme of the applied AP-MS workflow to identify MG132-enriched Rmnd5a-HCIPs in HEK-293 cells. (B) SAINT-network of Rmnd5a-HCIPs in cells treated with MG132 for 6 hr (confidence score ≥0.9, FC ≥ 4, n = 2). The GID subunits are labeled in light blue and remain stably associated in the presence of MG132. Constitutive HCIPs that were recovered in control and MG132-treated samples are colored in green. Proteins and protein networks that are specifically associated with the GID complex in the presence of MG132 are highlighted in yellow. (C) Quantification of total peptide spectral matches (psm) measured for Rmnd5a-HCIPs in DMSO control vs. MG132-treated samples. Note that the transcription factor Hbp1 is specifically enriched upon proteasome inhibition. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation experiment (HA-IP) using HEK-293 cells stably expressing HSS-Armc8 demonstrates specific interaction of the mitochondrial protease HTRA2 with the GID complex. (E) Immunoprecipitation and subsequent immunoblot analysis of HEK-293 cells expressing a doxycycline-inducible HSS-tagged construct of Hbp1. Note that Hbp1 not only binds its corepressor protein Sin3a but also multiple subunits of the GID complex.