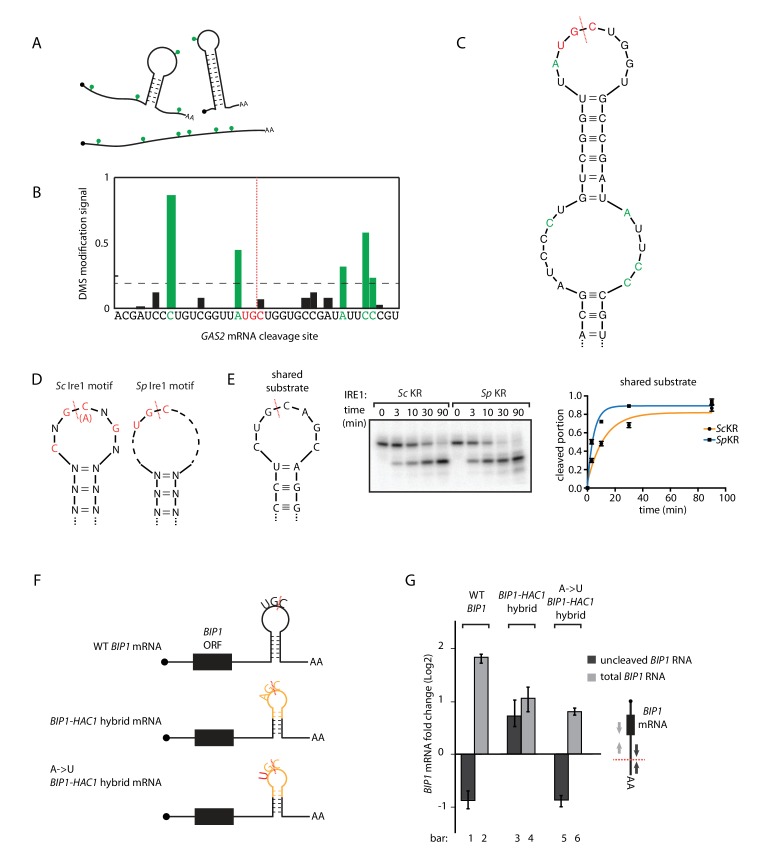
Figure 3. S.pombe and S. cerevisiae Ire1 recognize distinct RNA sequence and structural features.
(A) Illustration of RNA structural mapping by DMS modifications. Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) allows detection of unpaired adenine and cytosine RNA bases (green dots). (B) The normalized DMS modification signals near the Ire1 cleavage site on S. pombe GAS2 mRNA (cleavage site is indicated by the red dashed line). The positions with high DMS modification signals are labeled in green and the previously identified S. pombe Ire1 UG|C motif is labeled in red. (C) In sillico RNA secondary structure prediction of the Ire1 cleavage site on GAS2 mRNA. Structure prediction was constrained by forcing the positions with high DMS modification signals (green) to be unpaired. (D) RNA sequence and structural motifs recognized by the S. cerevisiae and S. pombe Ire1. (E) In vitro cleavage assay using an RNA hairpin derived from human XBP1 mRNA 3' splice site, which is predicted to be a shared substrate for S. cerevisiae and S. pombe Ire1 KR. The calculated kobs is 16.7 ± 2.3 × 10−4 s−1 for S. cerevisiae Ire1 KR and 38.9 ± 4.0 × 10−4 s−1 for S. pombe Ire1 KR. (F) Illustrations of the S. pombe BIP1 mRNA variants and (G) their uncleaved (dark grey) or total (light grey) mRNA fold change upon ER stress in S. pombe cells. Experiments were done in triplicates.