Figure 3.
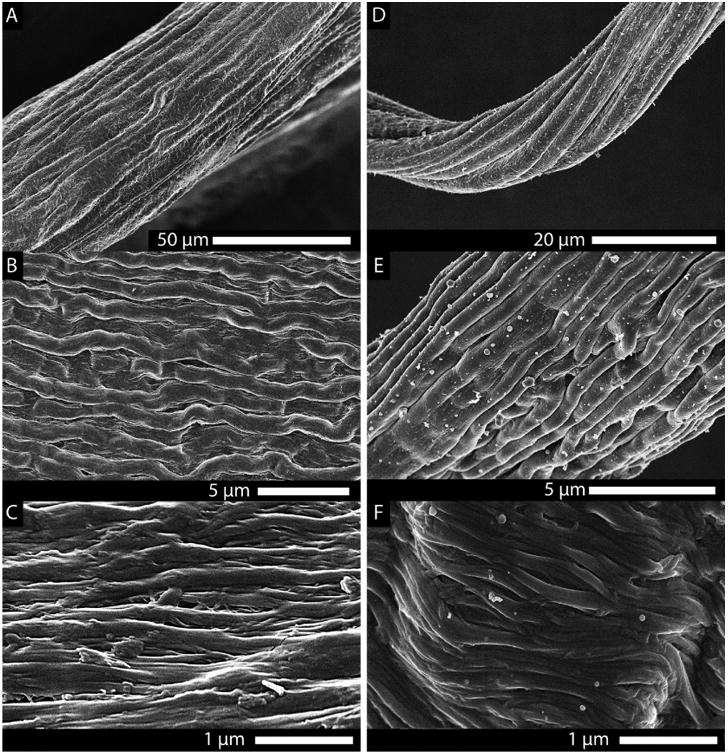
Scanning electron images of the spontaneously formed hierarchical substructure of the drawn collagen fibers. (A–C) Structure of a drawn telo-collagen fiber at progressively increasing magnification. (D–F) Drawn telo-fiber from a solution that contained 2% decorin. Both fibers displayed an impressive hierarchical morphology reminiscent of native tendon. However, the effect of the addition of decorin (a small leucine-rich proteoglycan found in the ECM, known to affect collagen fibril morphology) was apparent at the level of the individual collagen fibrils [(C) no decorin vs (F) decorin]. As seen in vivo, decorin appears to reduce the number of lateral associations between the fibrils in vitro, as well.
