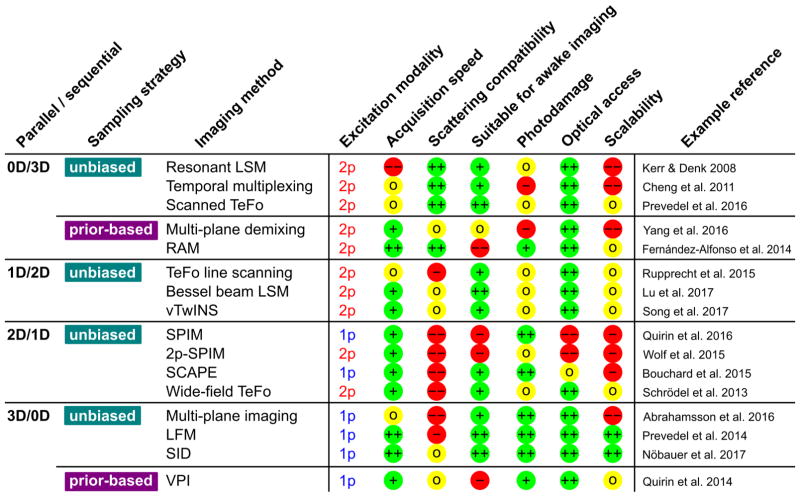
Figure 3.
Overview of the categories and key imaging properties of the available techniques for functional optical imaging, and their strengths and limitations. The modalities are categorized based on the acquisition mode(fully sequential, 1D parallel, 2D parallel and 3D parallel) and sampling strategy (unbiased/prior-based sampling). The key imaging properties, acquisition speed, scattering compatibility, suitability for awake imaging(including susceptibility to motion artifacts), photodamage, optical access, and scalability of the method, are rated with ++ (best, green), + (green), 0 (yellow), − (red), −− (worst, red). Example references for the techniques are provided.