Figure 5.
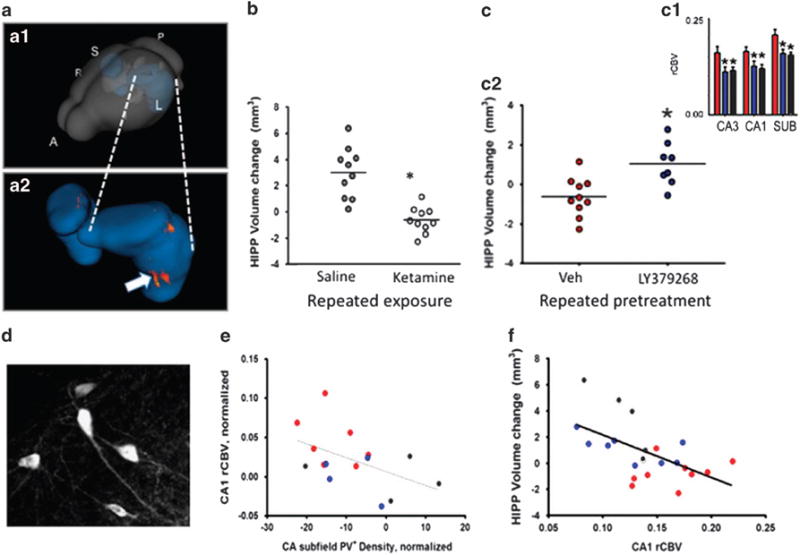
(a) Rendering of hippocampus within the mouse brain (A.1) and zoom-in of hippocampus (A.2) showing area of greatest morphological change produced by repeated ketamine treatment. (b) Repeated ketamine exposure (16 mg/kg, 3 × per week, 4 weeks)(open circles) blocks the normal growth of the hippocampus across the transition to adulthood in mice, leading to a reduction in volume relative to saline controls (gray circles). (c) Mice receiving repeated treatments with saline only (gray bars and circles), ketamine with saline pre-treatment (red) or ketamine with pre-treatment with the mGlurR 2/3 agonist LY347268 (blue). LY347268 co(pre)-treatment blocks the increase in basal CBV (c1) and relative loss of hippocampal volume (c2) produced by repeated ketamine exposure. (d). Parvalbumin expressing neurons in dorsal hippocampus of the mouse. (e) Correlation between PV+ neuron density and CA1 CBV; loss of PV+ interneurons is associated with increased CBV. (f). Hippocampal volume loss correlates with increases in CBV.
