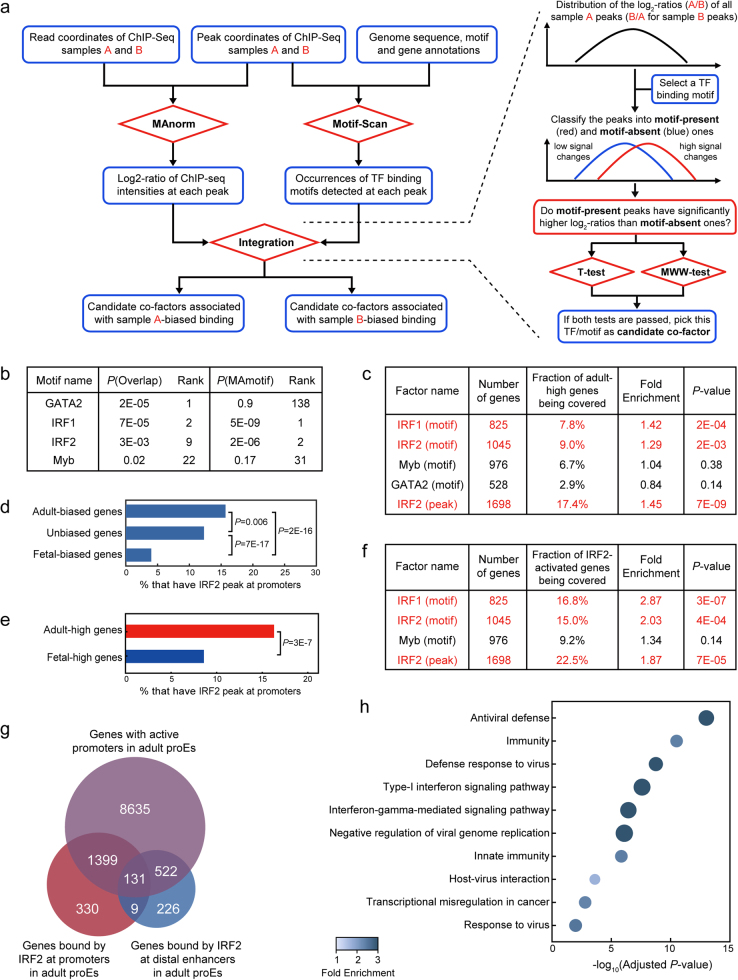
Fig. 1. Using MAmotif to compare the H3K4me3 ChIP-seq data of adult and fetal proEs.
a The overall workflow of MAmotif toolkit for comparing two ChIP-seq samples of the same chromatin-associated protein but from different cell types (a detailed introduction of the workflow and implementation of MAmotif toolkit and its Motif-Scan module can be found in Supplementary information and Supplementary Fig. S1b-f). Of note, MAmotif can also utilize TF binding information from other resources such as ChIP-seq data, instead of the TF binding motifs detected by its Motif-Scan module. b The top JASPAR motifs predicted by MAmotif and traditional overlap-based approach that are significantly associated with the adult-biased H3K4me3 promoter peaks compared to fetal proEs. c The overlap between adult-high genes and genes covered by the H3K4me3 promoter peaks of adult proEs that contain IRF1/2, MYB, GATA2 motifs, and IRF2 ChIP-seq peaks of adult proEs, respectively. d Fractions of adult-biased, fetal-biased, and unbiased H3K4me3-associated genes that have IRF2 peaks at their promoters. e Fractions of adult and fetal-high genes that have IRF2 peaks at promoters. Here the P-values shown in d and e were calculated by two-tailed Fisher’s exact test using hypergeometric distribution. f The overlap between IRF2-activated genes (genes downregulated after IRF2 knockdown in adult proEs) and genes covered by the H3K4me3 promoter peaks of adult proEs that contain IRF1/2, MYB motifs, and IRF2 ChIP-seq peaks, respectively. g Venn diagram shows the overlap between the genes with active promoters in adult proEs (covered by H3K4me3 peaks and not by H3K27me3 peaks, a repressive histone mark) and the IRF2 promoter/enhancer-bound genes of adult proEs. h Gene ontology (GO) enrichment analysis of the IRF2 promoter-bound genes in adult proEs. Here, all the active promoter genes of adult proEs were used as background and P-values were corrected by the Benjamini–Hochberg procedure for multiple testing