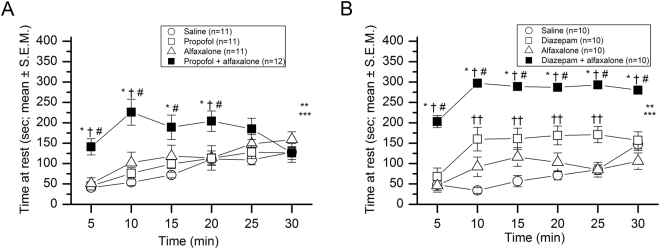
Figure 1.
Effects of combining alfaxalone with propofol, or with diazepam on mouse behavior. (A) A 30-min activity test was conducted immediately following i.p. injections of normal saline (20 Units), propofol (50 mg/kg), alfaxalone (30 mg/kg), or the combination of propofol (50 mg/kg) + alfaxalone (30 mg/kg), to determine drug effects on time at rest (absence of movement) as a function of post-injection time (5-min blocks) across the test session (means ± S.E.M.; n = 11–12 mice per treatment group). A repeated measures (rm) ANOVA revealed a significant drug effect (**p = 0.0005) and drug × time interaction (***p < 0.00005), with the propofol + alfaxalone mice exhibiting significantly increased time at rest compared to the single drug/saline control groups on average across the test session. Significant between-groups comparisons are shown for these contrasts: saline vs. propofol + alfaxalone at 5, 10, 15 (*p < 0.003), and 20 (*p = 0.031) min post-injection; alfaxalone vs. propofol + alfaxalone at 5, 10 (†p < 0.002), and 20 (†p = 0.038) min; and propofol vs. propofol + alfaxalone at 5, 10 (#p < 0.0002), and 15 and 20 (#p < 0.040) min. No significant differences were observed for the contrasts involving the saline vs. propofol or saline vs. alfaxalone groups. (B) A separate study was conducted on an independent cohort of naïve mice to examine the potential sedating drug effects following i.p. injections of normal saline (20 Units), diazepam (4 mg/kg), alfaxalone (30 mg/kg), or the combination of diazepam (4 mg/kg) + alfaxalone (30 mg/kg) on time at rest (n = 10 for each group). An rmANOVA yielded a significant drug effect (**p < 0.00005) and drug × time interaction (***p = 0.0004), with the diazepam + alfaxalone treated mice having significantly greater times at rest compared to the saline, alfaxalone, and diazepam groups on average across the session. Between-groups comparisons conducted within these contrasts showed robust differences between each of the single drug/saline control groups relative to the diazepam + alfaxalone treated mice for every post-injection time (5–30 min) interval (p < 0.0002; for the comparisons involving saline (*), alfaxalone (†), or diazepam (#), respectively). The diazepam group also had significantly increased rest times relative to the saline control mice, with pair-wise comparisons revealing significant differences at 10, 15, 20, and 25-min post-injection (††p < 0.003).