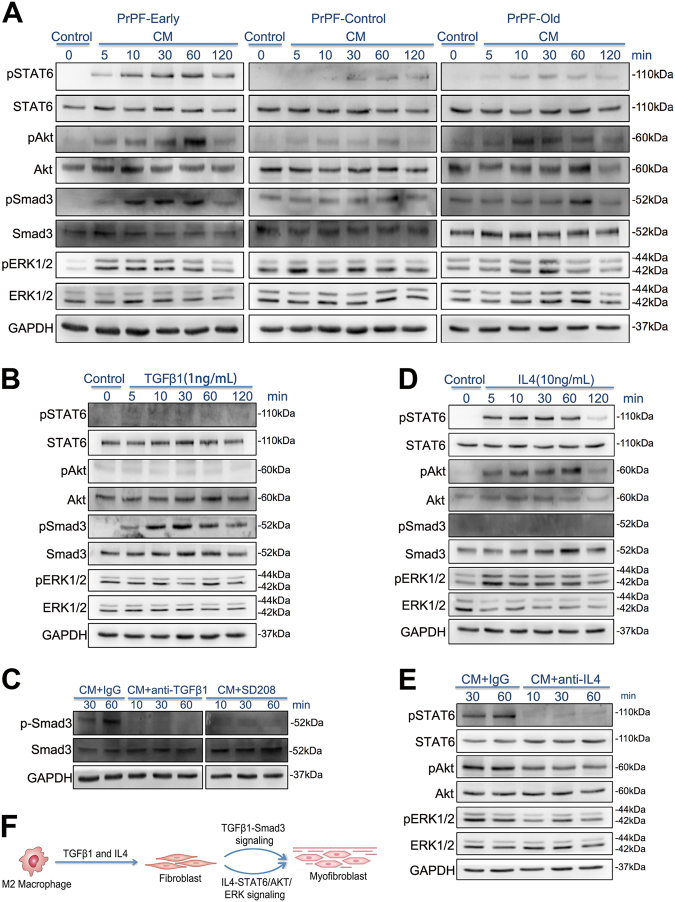
Fig. 6. Mechanisms underlying M2 macrophage-mediated development of myofibroblast phenotype in different primary prostate fibroblasts (PrPFs).
a SMAD3, STAT6, AKT and ERK phosphorylation levels in PrPF-early, PrPF-control and PrPF-old cells treated with the conditioned media (CMs) obtained from the THP-1-derived M2 macrophage–fibroblast co-cultures. b SMAD3, STAT6, AKT and ERK phosphorylation levels in PrPF-early, PrPF-control and PrPF-old cells treated with 1 ng/ml TGFβ1. c SMAD3 phosphorylation levels in PrPF-early cells following the treatment with CM pretreated for 3 h with 1 μg/ml anti-TGFβ1 antibody. Additionally, PrPF-early cells were pretreated with 1 μM SD208, a small-molecule ALK5 inhibitor of the TGFβ1R1/SMAD2/3 interaction, for 3 h. IgG isotype antibody (1 μg/ml) was used as a control. d JAK/STAT6, PI3K/AKT, SMAD3 and MAPK/ERK signalling following the treatment with 10 ng/ml IL4 in PrPF-early cells. e STAT6, AKT and ERK phosphorylation following the antibody-induced inhibition of IL4 for 3 h, prior to the treatment of PrPF-early cells with these media. CMs pretreated with 1 μg/ml IgG isotype antibody were used as controls. f Schematic illustration of the mechanisms underlying M2 macrophage-induced development of myofibroblast phenotype through the activation of TGFβ1 and IL4 signalling