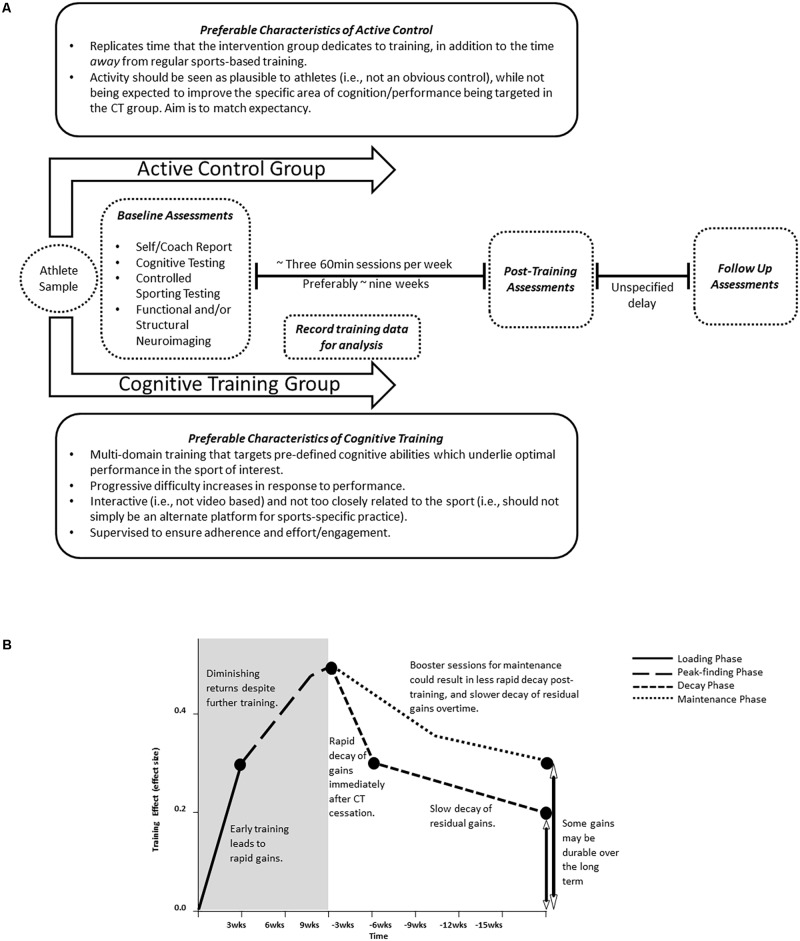
FIGURE 1.
(A) Example RCT design to asses CT for athletes. Brief outline of the preferable characteristics of the training and control groups, duration and frequency of the intervention and the types of assessments that should be administered. (B) Assumed therapeutic effect of CT overtime. Training (gray) initially produces rapid gains during the loading phase, which then begin to plateau during the peak-fining phase. Once training is ceased (white), during the decay phase, gains decay rapidly and then gradually over time. However, if a maintenance phase comprising of booster sessions is implemented during the decay phase, then gains may be durable over a longer period of time. In any case, training will result in a higher level of cognition when compared to baseline. Image adapted from Figure 3 in Lampit et al. (2014a).