Figure 4.
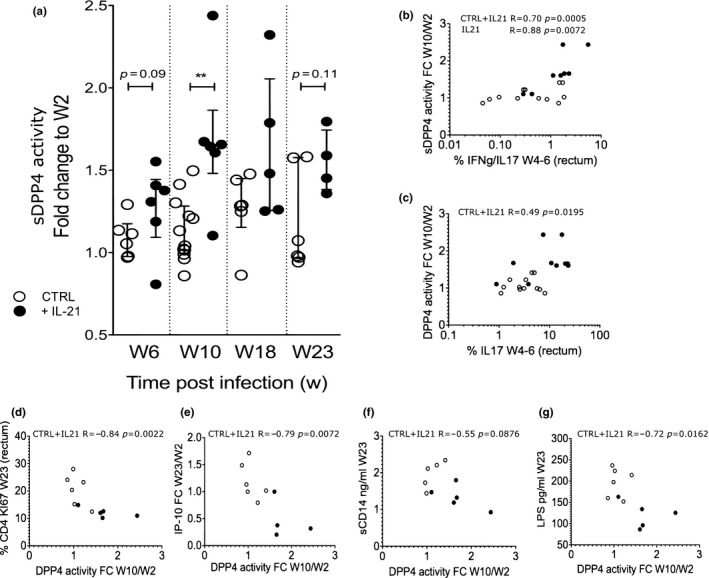
sDPP4 dynamics in blood after IL‐21 immunotherapy of SIV‐infected macaques. (a) sDPP4 activity in blood was measured in a longitudinal analysis before initiation of IL‐21 therapy (week 2 p.i.), at the end of IL‐21 treatment (week 6 p.i.) and after IL‐21 treatment (Weeks 10, 18 and 23 p.i.). The ratio of pre‐ and post‐treatment sDPP4 levels are shown. (b and c) IL‐17+ and IL‐17+ IFN‐•+ cells were measured in rectal biopsies on week 4 and week 6. (b) Correlation between the percentage of intestinal IL‐17+ IFN‐•+ cells and the plasma sDPP4 activity (fold change from week 2 to week 10) (c) Correlation between the percentage of intestinal IL‐17+ cells and plasma sDPP4 activity (fold change from week 2 to week 10). (d‐f) Correlation between sDPP4 activity in blood (fold change between week 2 and 10) and levels of (d) Ki67+ CD4+ T cells in gut (e) blood IP‐10 levels (f) blood sCD14 and (g) blood LPS after IL‐21 therapy cessation at week 23 p.i. For graph a, the Wilcoxon non‐parametric test was used; for graphs b to g, the Spearman non‐parametric correlation. The median and interquartile range are shown in graph a. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. Six rhesus macaques infected with SIVmac and treated with IL‐21 and six rhesus control macaques infected with SIVmac were analysed. CTRL: control monkeys; +IL‐21: IL‐21‐treated monkeys.
