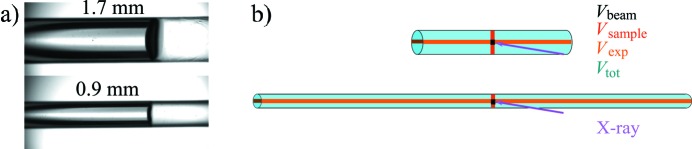
Figure 1.
(a) Magnified images of the two types of horizontal capillaries placed in the sample changer, loaded with a solution (side view), that can be held fixed in the beam (for stationary SAXS measurements) or can be flowed left to right during X-ray exposure. (b) The scheme of the accessible sample volume in the different geometries. Here, black squares mark the position and size of the X-ray beam, and represent the focal volume V beam of the sample exposed to the beam; the red rectangles indicate V sample; the orange rectangles indicate the total volume exposed V exp when flowing the sample; the total loading volume V tot is shown in blue. The arrows indicate the direction of the X-ray beam propagation. Both capillaries in (b) have the same total sample volume V tot.