Figure 1.
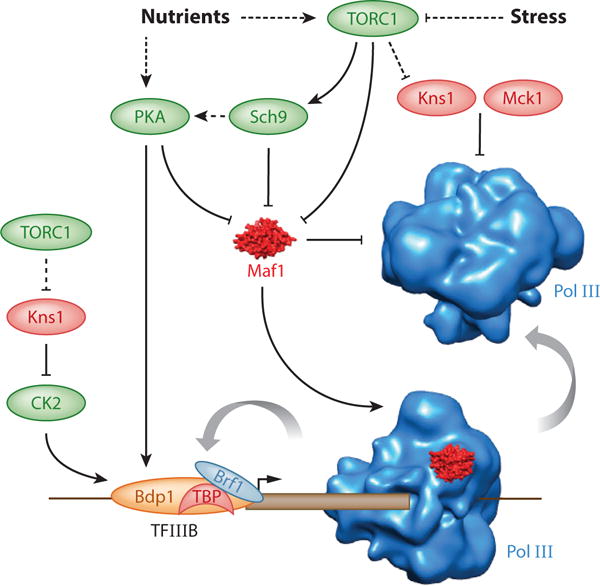
Signaling to the RNA polymerase III system in yeast. The scheme shows the known signaling kinases that mediate the response to nutrients and stress and their targets. Kinases that function to promote or repress transcription are shown in green and red ovals, respectively. Direct and indirect interactions/effects are represented by solid and dashed lines, respectively. Surface models of human Maf1 (red) and the yeast PolIII-Maf1 complex (15) are shown. Pol III is depicted on a tRNA gene with Maf1 positioned according to Vannini et al. (15). Large arrows indicate alternate fates of Pol III at the terminator, i.e. Maf1-resistant recycling or dissociation from the DNA. Dephosphorylation of Maf1 is known to involve PP4 and PP2A (not shown). Rpc53 phosphorylation by Kns1 and Mck1 is represented targeting free Pol III, but could also occur on the transcribing polymerase.
