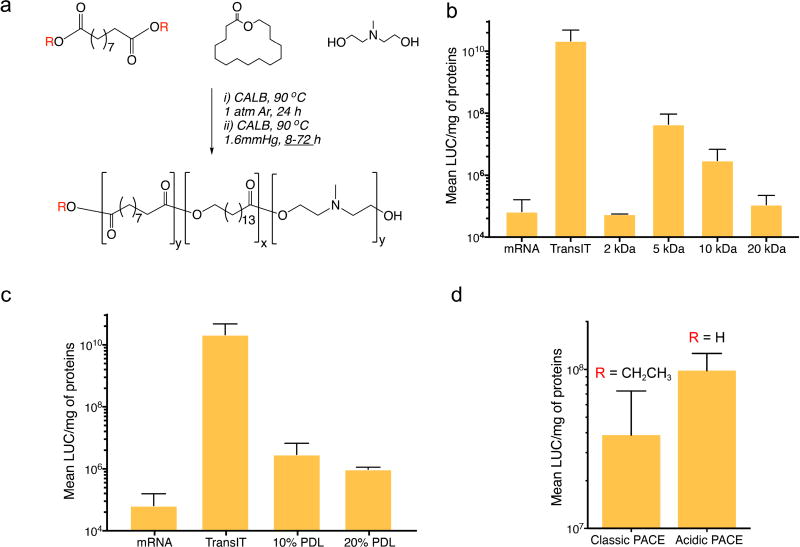
Figure 1. Synthesis of a PACE library for mRNA delivery.
(a) PACE synthesis was modified to vary different parameters in the final polymer. Diethyl sebacate (R = CH2CH3), or sebacic acid (R = H) were used to make classic (ester/OH) ended or acidic (COOH/OH) ended PACE, respectively. With classic PACE, the duration of the second step of the synthesis was varied from 8 to 72 h to vary the MW. The PDL content (10% or 20%) was varied to modify the polymer hydrophobicity. (b) Screening of MW using classic PACE with 10%PDL content: transfection efficiency increased when the MW was decreased up to 5 kDa, while further decrease of the MW to 2 kDa decreased transfection efficiency. (c) Screening of PDL content using a 10 kDa classic PACE polymer: no effect of PDL content was observed on mRNA transfection efficiency. (d) Transfection efficiency of acidic PACE and Classic PACE with MW of 5kDa at 10% PDL content: transfection efficiency is increased for acidic PACE compared to classic PACE. Results are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments run in duplicate.