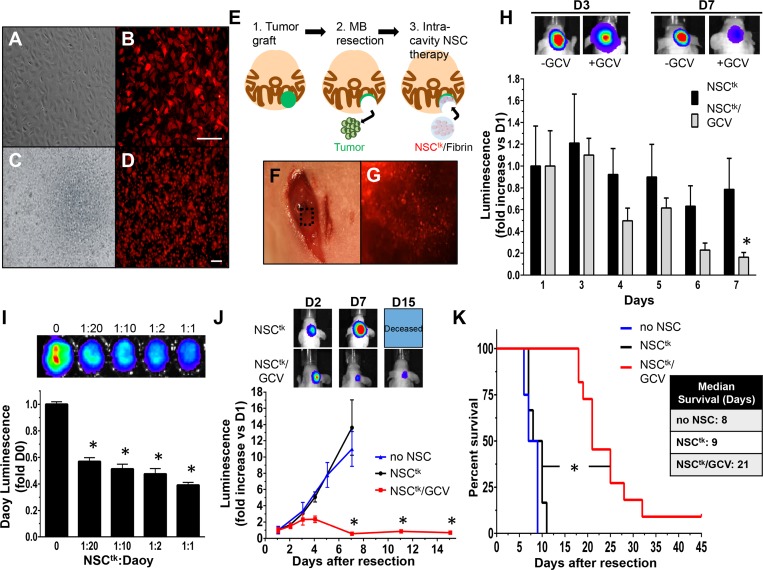
Fig 4. Therapeutic NSCs delivered within the resection cavity regress and delay re-growth of post-surgical MB.
White light and fluorescent images of NSC expressing TK (NSCtk) in culture (A, B) or mixed with fibrin matrix (NSCtk/fibrin) (C, D), illustrate high transduction efficiency and efficient expression of the construct. Depiction of the in vivo therapy schema, in which tumors were grafted within the cerebellum, resected and treated with therapeutic NSCtk/fibrin (E). Representative white light (F) and fluorescent (G) images confirm NSCtk/fibrin implanted within the resection cavity. NSCtk/fibrin persist longer in the brain without systemic administration of GCV (NSCtk) compared to with systemic administration of GCV (NSCtk/GCV) (H). Representative BLI images of NSCtk and NSCtk/GCVmice at days 3 and 7 post-surgery are shown above. Daoy-GFPFL cells were seeded with varying concentrations of NSCtk (I). Tumor cell viability was measured by luminescence 24h after GCV administration. Summary graph and representative BLI show a significant reduction of tumor burden in NSCtk/fibrin+GCV-treated mice compared to control-treated (J; no NSC and NSCtk). NSCtk/fibrin with GCV treatment extended median survival two-fold compared to controls (9 vs. 21 days, log rank *P<0.0001, K). Original magnification: 40X (C, D), 100X (A, B). Scale bars = 100 μm. n = 4 per group in the panel H, n = 4 in no NSC and NSCTK, n = 7 in the NSCTK/GCV group in J-K.