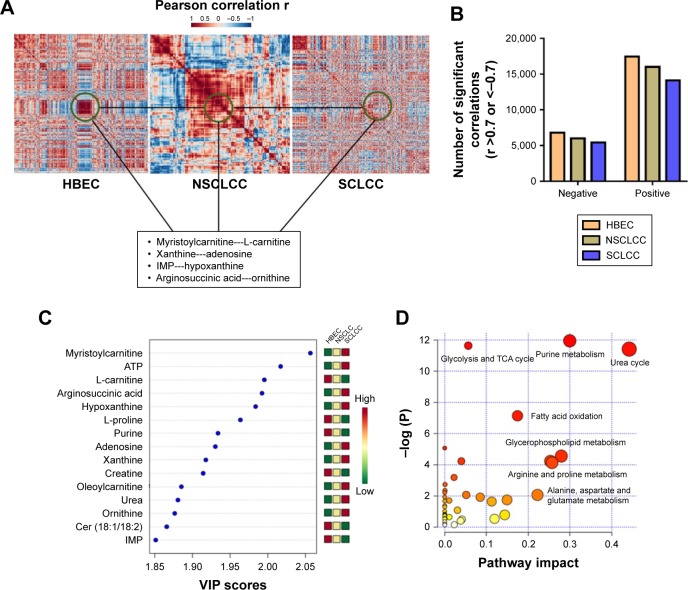
Figure 2.
The dramatic loss of correlations between metabolites in SCLCC.
Notes: (A) The distinct correlation patterns of metabolites between SCLCC, NSCLCC, and HBEC control cells. The examples of the loss of correlations between metabolites are highlighted in the box. (B) The number of significant positive correlations in SCLCC, NSCLCC, and HBEC. Pearson correlations coefficient r >0.7 (positive correlation) or <−0.7 (negative correlation) and p<0.05. (C) The top 15 most discriminating metabolites between SCLCC, NSCLCC, and HBEC. The metabolites are ranked by VIP scores. (D) The significantly altered metabolic pathways in SCLCC compared to NSCLCC and HBEC.
Abbreviations: ATP, adenosine triphosphate; HBEC, human bronchial epithelial cells; IMP, inosine monophosphate; NSCLCC, non-small lung cancer cells; SCLCC, small cell lung cancer cells; TCA, trichloroacetic acid; VIP, variable importance in projection.