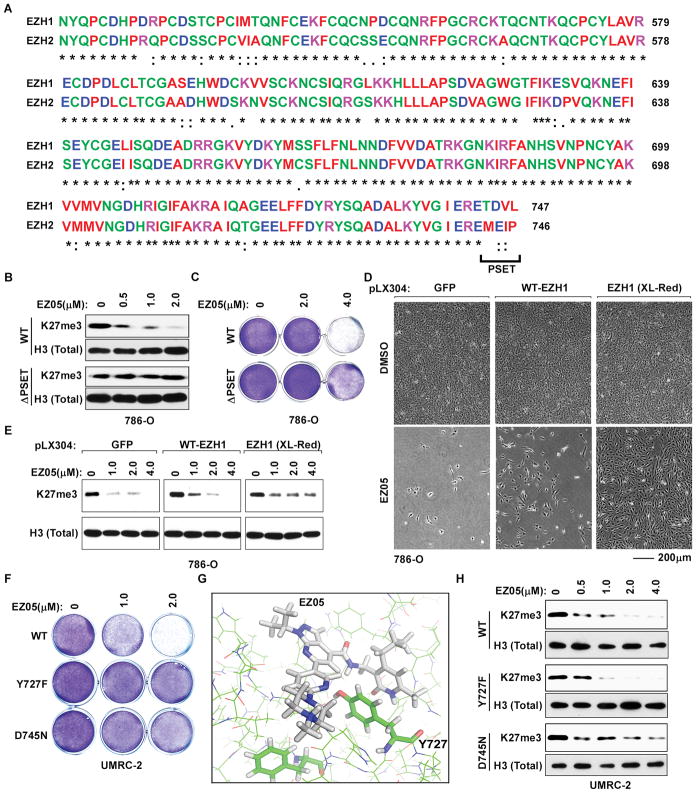
Fig. 5. Antiproliferative effects of JQ-EZ-05 on VHL−/− ccRCC are on-target.
(A) Sequence alignment of EZH1 and EZH2 catalytic SET domains.
(B and C) Immunoblots (B) and crystal violet staining (C) of 786-O cells infected to exogenously produce wild-type or ΔPSET EZH1 and treated with the indicated amounts of JQ-EZ-05 for 3 days and 7 days, respectively.
(D and E) Photomicrographs (D) and immunoblots (E) of 786-O cells infected with a lentivirus encoding GFP, wild-type EZH1, or randomly mutagenized EZH1 (XL-Red) and treated with the indicated concentrations of JQ-EZ-05 for 3 days (E) or with either 4 μM JQ-EZ-05 or DMSO for 21 days (D).
(F) Crystal violet staining of UMRC-2 cells infected to exogenously produce the indicated EZH1 variants and treated with the indicated concentrations of JQ-EZ-05 for 10 days.
(G) Structural model of JQ-EZ-05 bound to wild-type EZH1.
(H) Immunoblots of UMRC-2 cells expressing EZH1 variants as in (F) treated with the indicated concentrations of JQ-EZ-05 for 3 days.