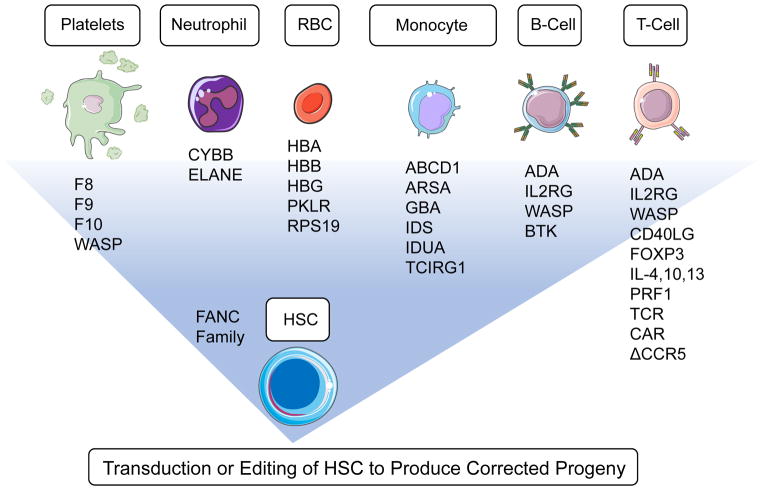
Figure 1. Overview of targets for gene therapy.
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) isolated from bone marrow can be modified ex vivo and transferred back to the recipient to produce functional, terminally-differentiated cells. Specific cellular targets and the relevant diseases and genes for gene therapy include the following: HSCs: Fanconi Anemia (FANC A–F). Platelets: Hemophilia A (Factor VIII (F8)); Hemophilia B (Factor IX (F9)); Factor X deficiency (Factor X (F10)); Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (Wiskott Aldrich Syndrome Protein (WASP)). Neutrophils: X-linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease (Cytochrome B-245 Beta Chain (CYBB)); Kostmann’s Syndrome (Elastase Neutrophil Expressed (ELANE)). Erythrocytes: Alpha-Thalassemia (Hemoglobin Subunit Alpha (HBA)); Beta-Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Disease (Hemoglobin Subunit Beta (HBB)); Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (Pyruvate Kinase, Liver and RBC (PKLR)); Diamond-Blackfan Anemia (Ribosomal Protein S19 (RPS19)). Monocytes: X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy (ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily D Member 1 (ABCD1)); Metachromatic Leukodystrophy (Arylsulfatase A (ARSA)); Gaucher disease (Glucosylceramidase Beta (GBA)); Hunter Syndrome (Iduronate 2-Sulfatase (IDS)); Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (Iduronidase, Alpha-L (IDUA)); Osteopetrosis (T-Cell Immune Regulator 1 (TCIRG1)). B Cells: Adenosine deaminase (ADA)-deficient Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)); X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (Interleukin 2 Receptor Subunit Gamma (IL2RG)); Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome (Wiskott Aldrich Syndrome Protein (WASP)); X-linked agammaglobulinemia (Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK)). T Cells: Adenosine Deaminase (ADA)-deficient Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (ADA); X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (IL2RG); Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Protein (WASP); X-linked Hyper IgM syndrome (CD40 Ligand (CD40LG)); IPEX Syndrome (Forkhead Box P3 (FOXP3)); Early Onset Inflammatory \Disease (Interleukin 4, 10, 13 (IL-4, 10, 13));Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (Perforin 1 (PRF1)); Cancer (Artificial T cell receptors (TCR), Cancer; Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)); Human immunodeficiency virus (C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 5 (CCR5)).