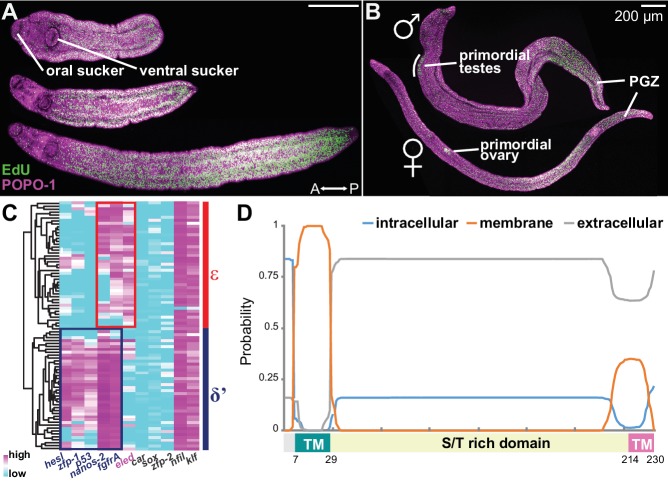
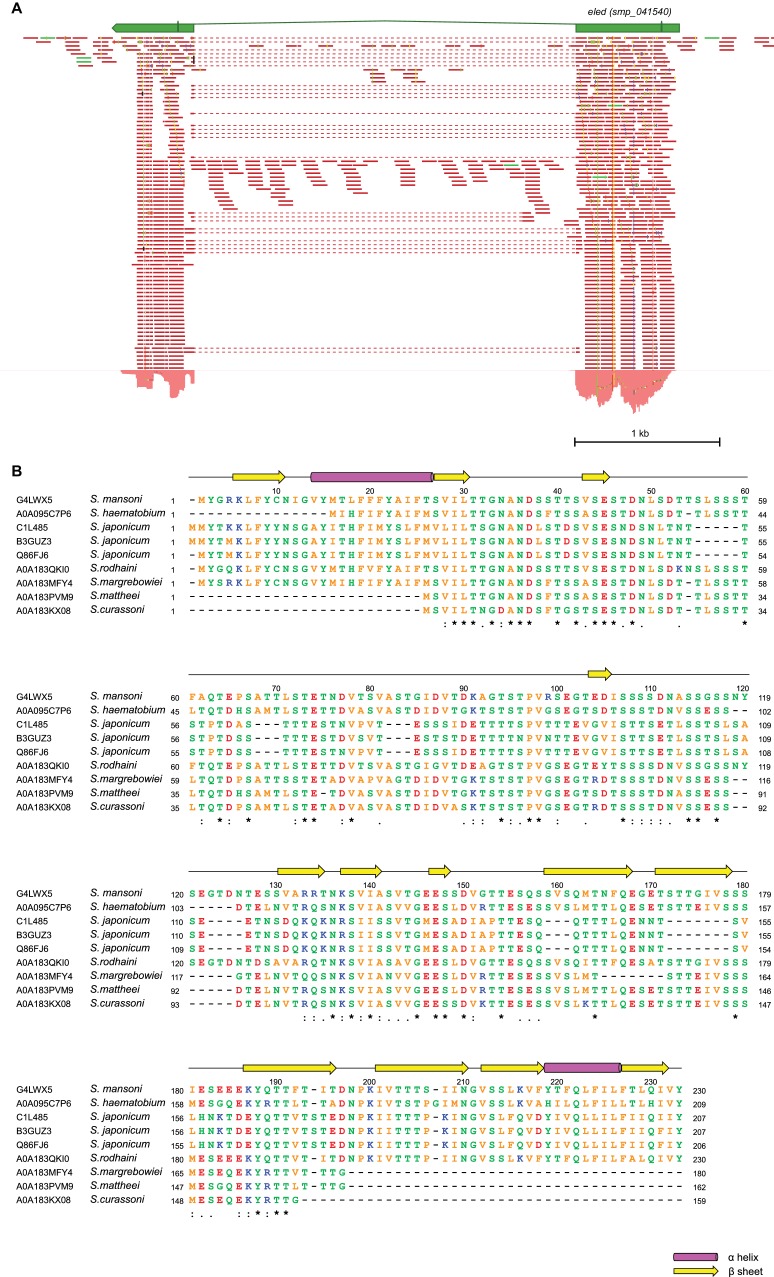
Figure 4. Emergence of a new stem cell class, ε, in juveniles.
(A–B) Distributions of EdU+ cells in three-week-old juveniles. Note the high density of EdU+ cells toward the posterior of the worms. (B) More mature males with partly developed lateral body extensions and females with a visible uterus display EdU+ cells in primordial gonads and the posterior growth zone (PGZ). (C) Hierarchical clustering of 85 juvenile stem cells distinguishes two major cell classes. Gene names in blue: cell class-dependent genes identified in the sporocyst stem cells; gene names in grey: top genes upregulated in juvenile stem cells compared to sporocyst stem cells. Expression levels were standardized gene-by-gene by mean-centering and dividing by the standard deviation of expressing cells. (D) Domain diagram of Eled, predicted by TMHMM 2.0 (Krogh et al., 2001). TM: transmembrane domain. S/T rich domain: extracellular domain enriched in serine/threonine.