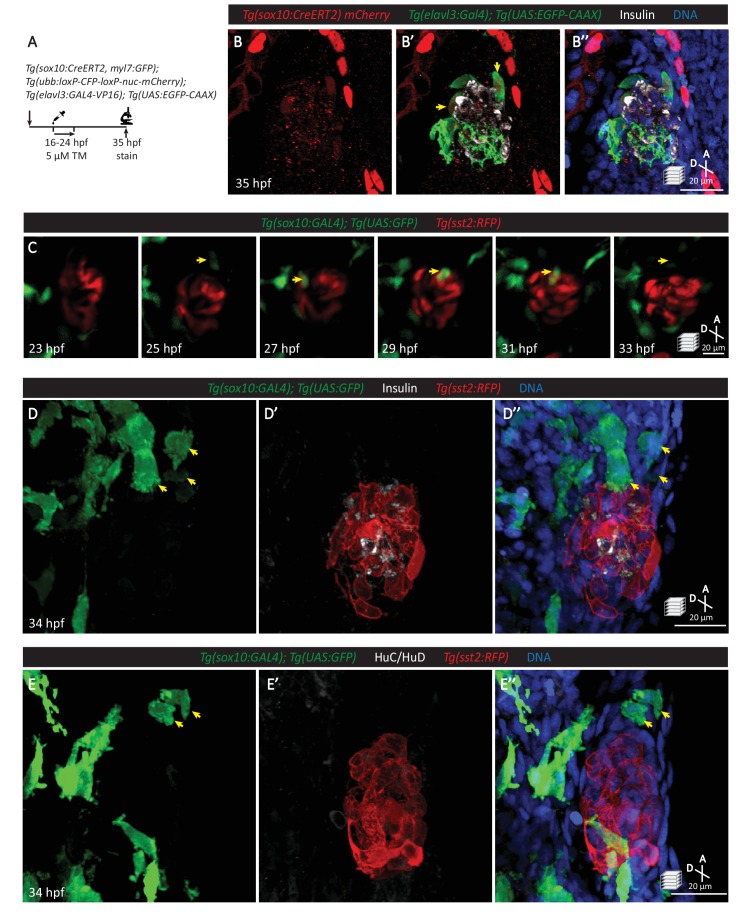
Figure 3. Neural crest cells are in close contact with pancreatic endocrine cells early in development.
(A) Lineage tracing of neural crest cells in Tg(sox10:CreERT2, myl7:GFP); Tg(ubb:loxP-CFP-loxP-nuc-mCherry); Tg(elavl3:GAL4-VP16); Tg(UAS:EGFP-CAAX) zebrafish following 5 µM tamoxifen treatment from 16 to 24 hpf and staining at 35 hpf. (B) Whole mount immunostaining at 35 hpf for mCherry (neural-crest-derived cells), GFP (elavl3-positive cells), Insulin (beta cells), and DAPI (DNA). (C) Confocal imaging of Tg(sox10:GAL4); Tg(UAS:GFP); Tg(sst2:RFP) zebrafish mounted in 0.5% agarose from 23 to 33 hpf. Yellow arrow points to a neural crest cell in close proximity to endocrine pancreatic cells and briefly contacting islet cells before migrating away. (D) Whole mount immunostaining at 34 hpf for GFP (sox10-positive cells), Insulin (beta cells), RFP (delta cells), and DAPI (DNA). Yellow arrows point to neural-crest-derived cells that were once in contact with the pancreatic islet. (E) Whole mount immunostaining at 34 hpf for GFP (sox10-positive cells), HuC/HuD (mature neurons), RFP (delta cells), and DAPI (DNA). Yellow arrows point to neural-crest-derived cells that were once in contact with the pancreatic islet.