Figure 4. PRMT1 inhibitor regulates the reciprocal recruitment of STAT3 and STAT5 to the IL-17 locus.
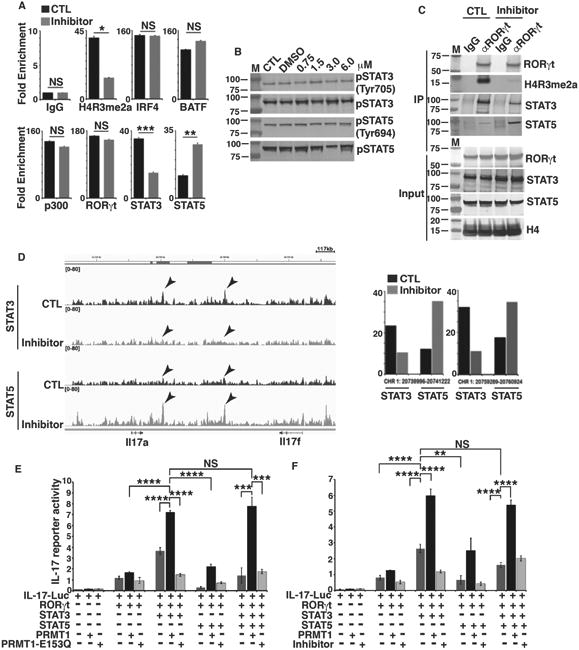
A) ChIP analysis of the enrichment of H4R3me2a, or indicated transcription factors in IL-17 promoter region in GFP+ fractions of CD4+ T cells differentiated under Th17 priming conditions in the presence (inhibitor) and absence (control, CTL) of PRMT1 inhibitor. B) Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylated or whole STAT3 and STAT5 in naïve CD4+ T cells differentiated under Th17 priming conditions in the presence and absence of indicated concentrations of PRMT1 inhibitor. C) Immunoblot analysis of indicated proteins from immune-complexes eluted from chromatin precipitates with control anti-IgG or RORγt antibody from naïve CD4+ T cells differentiated under Th17 priming conditions in the presence and absence of PRMT1 inhibitor. D) STAT3 and STAT5 DNA-binding peaks at IL-17 gene locus in CD4+ T cells differentiated under Th17 priming conditions in the presence and absence of PRMT1 inhibitor, as determined by ChIP-seq assay. Arrows indicate the locations of two most prominent peaks. Right panel is the quantitative value of arrow indicated peaks on left. E) Relative luciferase activity of IL-17 reporter in HEK 293T cells transfected with indicated expression plasmids. The luciferase activity is normalized to Renilla luciferase activity (mean ± sd). F) Relative luciferase activity of IL-17 reporter in HEK 293T cells transfected with indicated expression plasmids and/or presence of PRMT1 inhibitor. The luciferase activity is normalized to Renilla luciferase activity (mean ± sd). *P<0.05, (A, two-tailed unpaired t-test; E, F, One-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-analysis multiple comparison), NS: non-significant by unpaired t-test. B is the representatives of three independent experiments.
