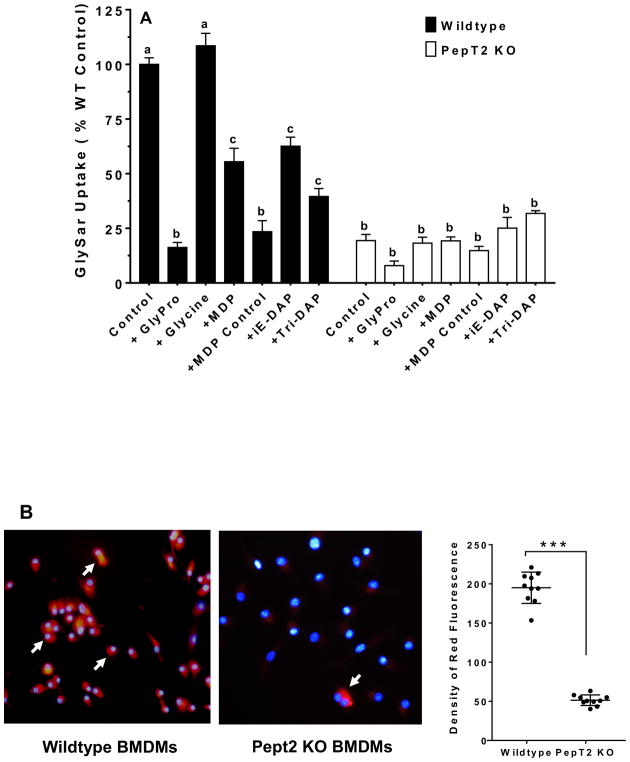
FIGURE 3.
GlySar and MDP-rhodamine uptake studies in BMDMs of wildtype and Pept2 knockout mouse. (A) effect of potential inhibitors on the uptake of 1.0 μM [3H]GlySar where GlyPro or glycine were present at 5 mM, and MDP (L,D-isomer), MDP control (L,L-isomer), r-iE-DAP or tri-DAP were present at 1 mM. GlySar uptakes were corrected for nonspecific binding using [14C]mannitol, and represented as % control, relative to wildtype mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SE (n=6) in which each experiment was performed in triplicate. Treatment groups with the same letter were not statistically different, as determined by ANOVA and Tukey’s test. (B) uptake of MDP-rhodamine in wildtype and Pept2 knockout mice. MDP-rhodamine (red) was marked by arrows and the nuclei (blue) were stained by DAPI (40× magnification). Density measurements are shown in the right-hand panel (LabWorks Image Acquisition and Analysis Software v4.5, UVP Inc, Upland, CA), and expressed as mean ± SE (n=10 cells). Statistical differences between the two genotypes were determined by an unpaired (two-sample) t-test. ***p ≤ 0.001.