Fig. 6.
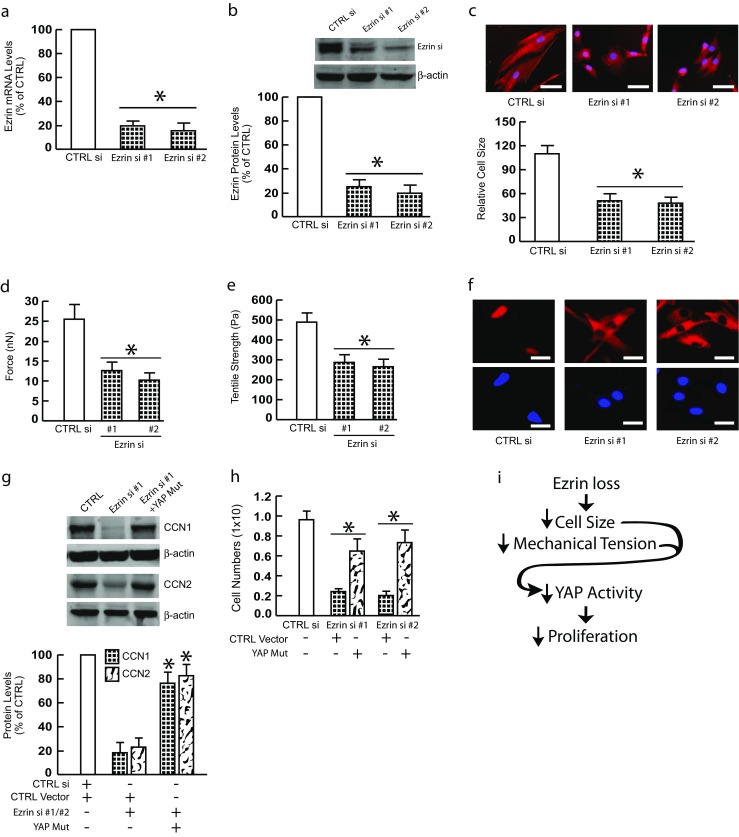
Ezrin regulates cell size/mechanical properties and YAP-dependent proliferation in neonatal foreskin human fibroblasts. Neonatal foreskin human fibroblasts were transfected with non-specific control siRNA or Ezrin siRNAs (20 nM) for 48 h. a Ezrin mRNA levels were reduced by Ezrin siRNAs. N = 4. b Ezrin protein levels were reduced by Ezrin siRNAs. N = 3. c Cell size was reduced by Ezrin siRNAs. Cells were stained with CellTracker® fluorescent dye. Red fluorescence delineates cell cytoplasm; blue fluorescence delineates nuclei. The relative cell surface areas were quantified by ImageJ. Bars = 50 μm. N = 3. d Cell traction force (nN) was reduced by Ezrin siRNAs. N = 4. e Cell tensile strength (Pa) was reduced by Ezrin siRNAs. N = 4. Mechanical properties were determined by atomic force microscopy (AFM) PeakForce Quantitative NanoMechanics mode and analyzed by Nanoscope Analysis software. f Impaired YAP nuclear translocation was determined by immunostaining. Images represent three independent experiments. Blue fluorescence delineates nuclei. Bar = 50 μm. g Restoration of YAP nuclear translocation reversed YAP target gene expression. Cells were transfected with non-specific control siRNA or Ezrin siRNAs or Ezrin siRNAs plus constitutively active YAP for 48 h. CCN1 and CCN2 protein levels were determined by Western blots. Protein levels were normalized by β-actin as a loading control. Insets show representative Western blots. N = 3. h Ezrin knockdown inhibits fibroblasts proliferation via impaired YAP activity. Cells were transfected with non-specific control siRNA or Ezrin siRNAs or Ezrin siRNAs plus constitutively active YAP for two days. Cells were harvested two days after transfection and 2.5 × 105 cells were cultured in 60 mm plates for six days. Cells were than harvested and counted. All data are expressed as mean±SEM, *p < 0.05 vs control. i Scheme summarizing the role of Ezrin in regulation of skin fibroblast size/mechanical properties and YAP-mediated proliferation (see Discussion for details)
