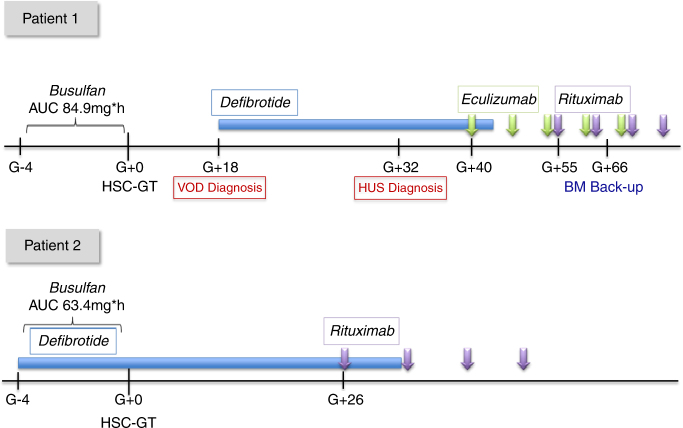
Fig. 1.
Treatment schedule of the 2 patients undergoing HSC-GT. Patient 1: Diagnosis of VOD on day +18 was based on the modified Seattle criteria: hepatomegaly and increased body weight >2%;. Reduced urine output and refractoriness to PLT transfusions preceded hepatomegaly and ascites; this confirms the importance of EBMT revised pediatric diagnostic criteria for VOD recently published (Corbacioglu S. et al.). In this case, the increase of D-dimer was documented very early in the course of VOD, while increase of hepatic necrosis enzymes (peak values ALT 617 UI/L, AST 1040 UI/L, LDH 759 UI/L), bilirubin (peak value of total bilirubin 2.67 mg/dL, direct 1.48 mg/dL) and need of ascetic fluid drainage followed the start of Defibrotide. Defibrotide (Defitelio) 25 mg/kg/day i.v. QID was given from d + 18 to d + 41 resulting in remission of all signs and symptoms of VOD. Diagnosis of TMA on d + 32 was based on relapse of refractoriness to platelet transfusions, increase in indirect bilirubin values (up to 3.02 mg/dl), reduction of haptoglobin, presence of schistocytes 2–3% in peripheral blood smear and urine protein/creatinine ratio (peak value >10). Anti-CHF antibodies were positive (1371 UI/ml), accompanied by a reduction of complement factors (C3 0.77 g/L, C4 0.07 g/L). Eculizumab (Soliris) 300 mg i.v. weekly for 4 doses was administered from d + 40, followed by 2 maintenance doses (300 mg i.v.) every 2 weeks. On d + 55, Rituximab 375 mg/m2 i.v. for 4 weekly doses was started due to persistent presence of anti-CFH and anti-platelet antibodies with low PLT counts. On d + 66, due to delayed hematological recovery, back-up reinfusion was performed. Patient 2: received prophylactic Defibrotide 25 mg/kg/day i.v. QID from d-4 before HSC-GT to d + 30. Rituximab 375 mg/m2 was administered from d + 26 for 4 doses, due to presence of anti-CHF and anti-PLT antibodies. He did not develop signs of VOD or TMA