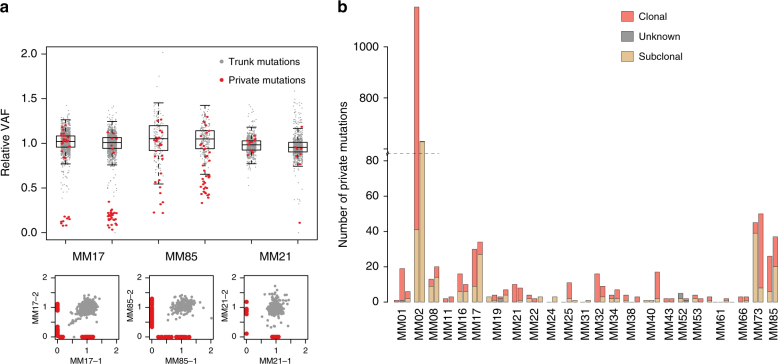
Fig. 4.
Cellular prevalence of mutations. a Relative variant allele frequency (rVAF); that is observed variant allele frequency corrected by tumor purity, local total copy number and estimated number of mutated alleles, for mutations in six representative samples from three patients. In theory, relative VAF is equivalent to cellular prevalence of the mutations. Mutations are colored according to presence in other lesions; gray, trunk mutations; red, private mutations. Boxes with whiskers are based solely on the trunk mutation relative VAFs and span the interquartile range (IQR), with whiskers extending to 1.5 times the IQR of the trunk relative VAF from the upper and lower bounds of the boxes. The three lower panels show examples of pairwise comparisons. b Private mutations were classified according to status as clonal or subclonal, where subclonal mutations are those whose relative VAF is below the whiskers in a. Mutations below half the median relative VAF and above the subclonality threshold are defined as unknown