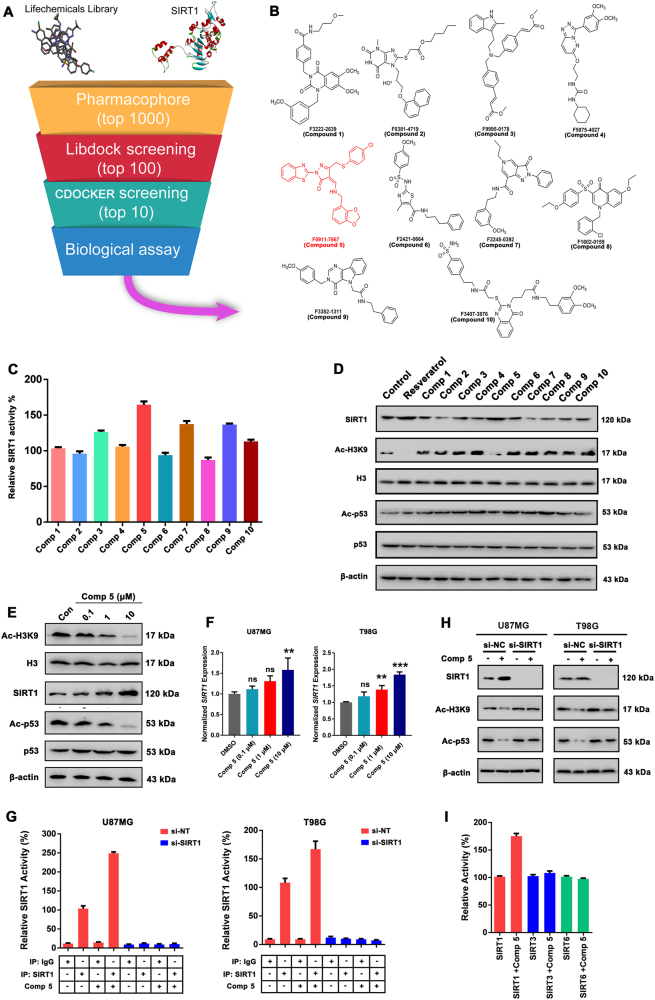
Fig. 2. Discovery of novel SIRT1 activators.
a Virtual screening schematic model for the discovery of novel SIRT1 activators. b Chemical structure of the top 10 candidate SIRT1 activators. c The top 10 candidate compounds (1 μM) were screened for deacetylase activity by SIRT1 activity assay. d U87MG cells were incubated with top 10 candidate compounds (1 μM) for 24 h, then detected by western blot for acetylated or total H3 or SIRT1 protein, as well as the acetylated or total p53. Resveratrol (1 μM) was used as a positive control for SIRT1 activator. e U87MG cells were incubated with 0.1, 1, 10 μM Comp 5 for 24 h, then detected by western blot for acetylated or total H3 or SIRT1 protein, as well as the acetylated or total p53. β-actin was used as a loading control. f The mRNA expression levels of SIRT1 in U87MG and T98G cells treated with 0.1, 1, 10 μM Comp 5 were quantified by real-time PCR. The values obtained from the control group were set at 1.0. Values were means ± SD, n = 3 per group. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01. g The cellular SIRT1 deacetylase activities of Comp 5 were determined by SIRT1 activity assay kit using cellular extracts obtained from normal or SIRT1-silenced U87MG and T98G cells. h U87MG and T98G cells were transfected with SIRT1 siRNA for indicated time and treated with Comp 5 for additional 24 h. The expression levels of SIRT1 as well as acetylated H3K9 or p53 were determined by western blot. i The in vitro SIRTs deacetylase activities of Comp 5 were determined by SIRT1, SIRT3, and SIRT6 activity assay kits