Figure 5.
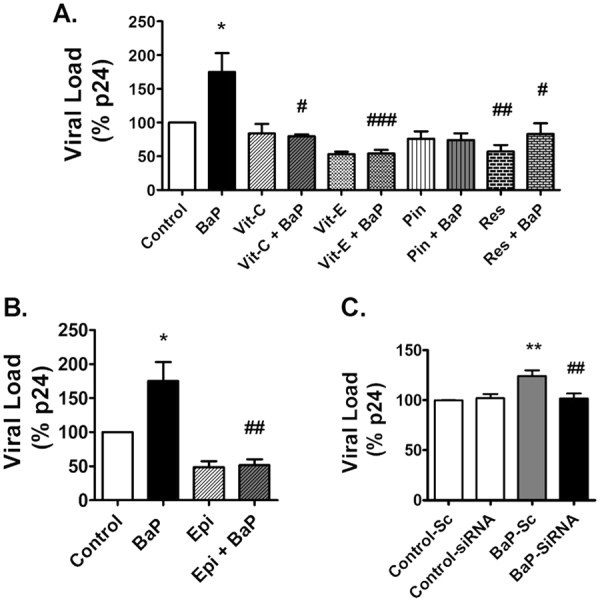
Treatment of antioxidants and CYP1A1 inhibitors reduce HIV-1 replication in U1 cells due to BaP exposure. U1 cells were concomitantly treated with BaP (1 µM) and antioxidants [vitamin C (100 µM) and vitamin E (100 µM), pinostilbene (2 µM), and resveratrol (50 µM)] (A) or CYP1A1 inhibitor ellipticine (1 µM)] (B) for 3 days. Prior to BaP treatment, the CYP1A1 gene was knocked down in the U1 cells using siRNA specific to CYP1A1. (C) The cells were then treated with BaP (100 nM) for 3 days. After the treatment, supernatants were collected to determine the viral load using the p24 ELISA assay. HIV-1 replication significantly increased with 3-days exposure of BaP (1 µM), which was rescued by all the antioxidants (vitamin C and E, and resveratrol) as well as the CYP1A1 inhibitor, ellipticine . The knock-down of the CYP1A1 gene also rescued HIV-1 replication in BaP-exposed U1 cells. The data were obtained from the mean of at least three independent experiments. * and ** represents p ≤ 0.05 and p ≤ 0.005 compared with the control group while #,## and ### represents p ≤ 0.05, p ≤ 0.005 and p ≤ 0.0005, respectively, compared to the BaP-treated groups.
