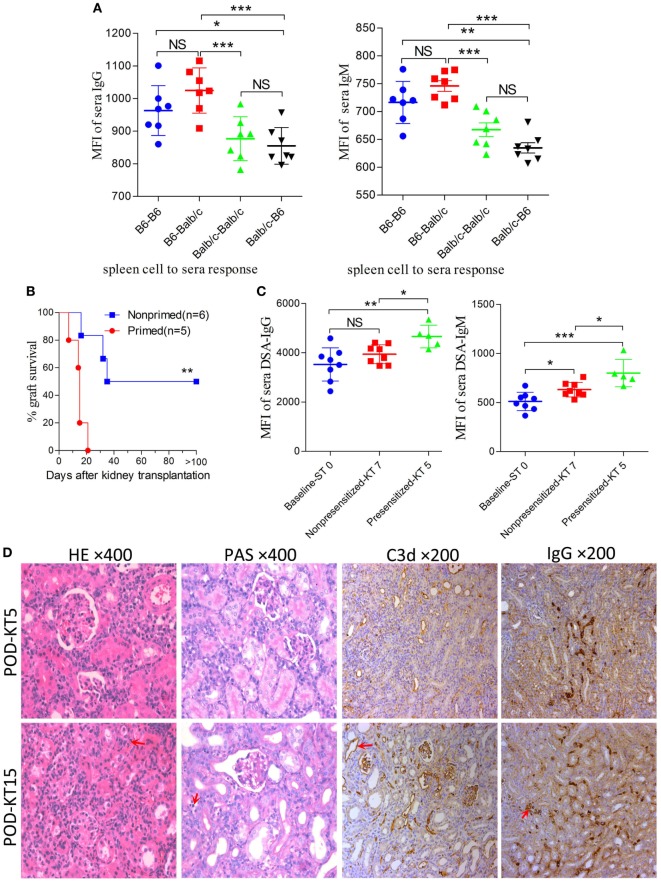
Figure 4.
Improving survival by establishing an antibody-mediated rejection (AMR) model in C57BL/6 to Balb/c mice. Balb/c recipient mice were primed with C57BL/6 skin grafts for 4 days prior to receiving C57BL/6 kidney grafts. Balb/c mice receiving C57BL/6 kidneys without skin grafting acted as the nonprimed controls. Serum donor-specific antibody (DSA) levels were detected by flow cytometry and expressed as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). The DSA data represent mean ± SD of at least five independent samples (Student’s t-test). ST0 = day 0 before skin transplant, KT5, KT7, and KT15 = day 5, 7, and 15 after kidney transplant, respectively. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. NS, no significant difference. (A) Donor-reactive antibody baseline levels in C57BL/6-Balb/c were higher than those in Balb/c-C57BL/6. (B) Kidney graft mean ± SD survival times were >33.8 ± 9.3 and 14.4 ± 5.0 days in the nonprimed and primed groups, respectively (Log-rank test). (C) DSA levels of IgG and IgM in the sera from recipients in the primed group were significantly increased on KT5 compared to the baseline ST0, and were higher than the levels on KT7 in the nonprimed group. (D) Sections of kidney grafts were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), ×400; and for the deposition of IgG and C3d, ×200. AMR histological features of tubular injury, peritubular capillary (PTC) dilation, and capillaritis, deposition of IgG and C3d in PTC could be identified on KT5 and KT15 in the skin-primed group. Arrows in the HE and PAS staining indicate the PTC and capillaritis. Arrows in the IgG and C3d staining indicate the positive depositions in PTCs.