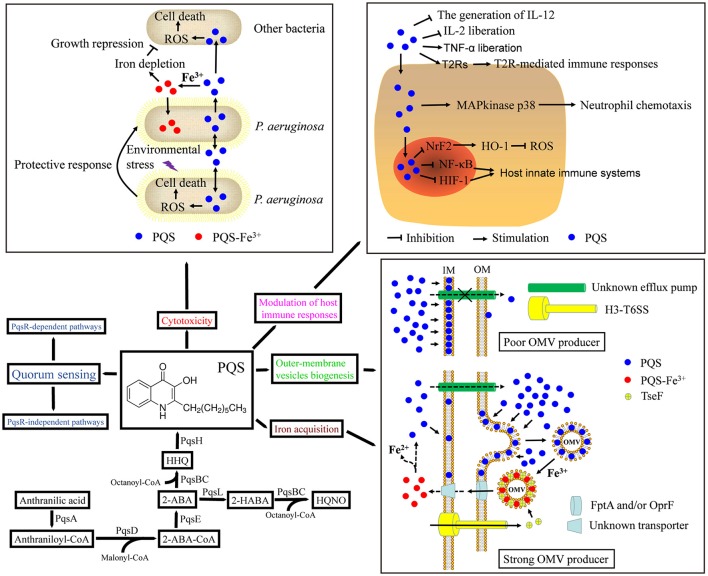
Figure 1.
Biosynthetic pathway and multifunctionality of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS). Biosynthesis of HHQ requires PqsABCDE proteins. The mono-oxygenase PqsH then converts HHQ to PQS. PQS has been implicated in quorum sensing, iron acquisition, cytotoxicity, outer-membrane vesicle biogenesis, and modulation of the host immune response. See text for details. ROS, reactive oxygen species; IL-12, interleukin-12; IL-2, interleukin-2; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; T2Rs, taste family 2 bitter receptor proteins; NrF2, transcription factor NrF2; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; NF-κB, nuclear transcription factor-κB; HIF-1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; OM, outer membrane; IM, inner membrane; OMV, outer membrane vesicle; the dotted lines indicate a hypothesis. A second mono-oxygenase, PqsL, is required together with the pqsABCDE gene products for the synthesis of HQNO. Intermediates and products of the alkylquinolone biosynthetic pathway: 2-ABA-CoA, 2-aminobenzoylacetyl-coenzyme A; 2-ABA, 2-aminobenzoylacetate; 2-HABA, 2-hydroxylaminobenzoylacetate, HHQ, 2-heptyl-4-quinolone; HQNO, 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline-N-oxide; PQS, 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4-quinolone.