Figure 14.
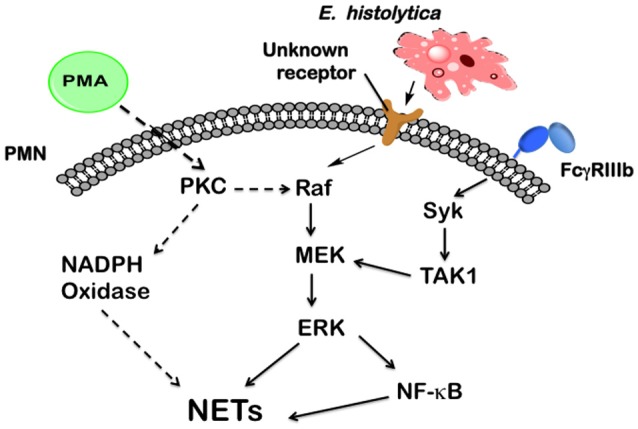
Model for signaling in neutrophils to induce NETosis after Entamoeba histolytica engagement. In human neutrophils, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) can directly activate (dashed arrows) protein kinase C (PKC), which in turn leads to activation of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. These kinases finally promote NETs formation. PKC is also required for NADPH-oxidase activation to form reactive oxygen species, which are required for NETs formation after PMA stimulation. In contrast, E. histolytica trophozoites are recognized by neutrophils via a, yet unknown, receptor, which connects to the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. Also the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is activated to promote NETs formation. The antibody receptor FcγRIIIb also induces NETs formation via spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) and transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), which connects to MEK (Alemán et al., 2016b). Other signaling molecules (not shown), such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), and p38 MAP kinase are not involved in E. histolytica signaling to NETs formation.
