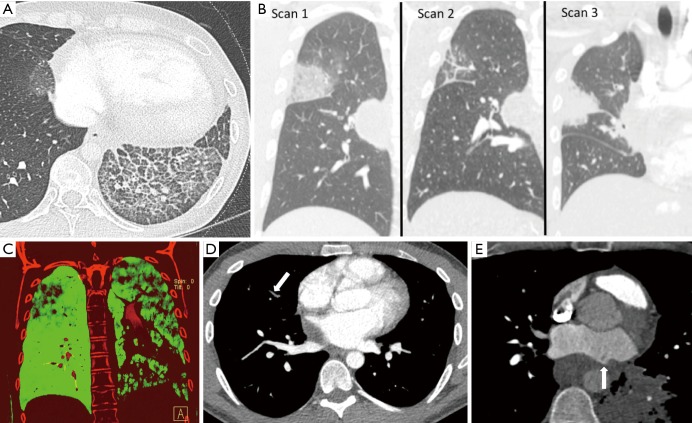
Figure 5.
Indirect cross-sectional imaging findings of acquired pulmonary vein stenosis in an adult: lung edema, waxing and waning lung opacities, decreased perfusion to the lung that is drained by the stenosed vein, non-opacified peripheral pulmonary veins, and mixing artifact at the interface between the stenosed pulmonary vein and the left atrium. (A) Axial CT shows interlobular septal thickening, intralobular interstitial thickening, and ground-glass opacity in the left lower lobe; lung edema secondary to left inferior pulmonary vein stenosis (can be mistaken for lung infection or lung hemorrhage); (B) coronal CT images from serial CT scans demonstrate waxing and waning lung opacities in the right upper and right middle lobes secondary to right superior pulmonary vein stenosis (can be mistaken for lung infection or lung infarction from pulmonary embolism); (C) coronal dual-energy CT image in demonstrates decreased lung perfusion to the left upper, left lower, and right upper lobes secondary to left superior pulmonary vein stenosis, left inferior pulmonary vein stenosis, right superior pulmonary vein stenosis; (D) axial CT image shows nonopacification of the right upper lobe pulmonary veins secondary to right superior pulmonary vein stenosis (can be mistaken for pulmonary emboli); (E) axial CT image shows mixing artifact at the interface between the left superior pulmonary vein and the left atrium (arrow) secondary to left superior pulmonary vein stenosis (can be mistaken for thrombus).