Figure 3.
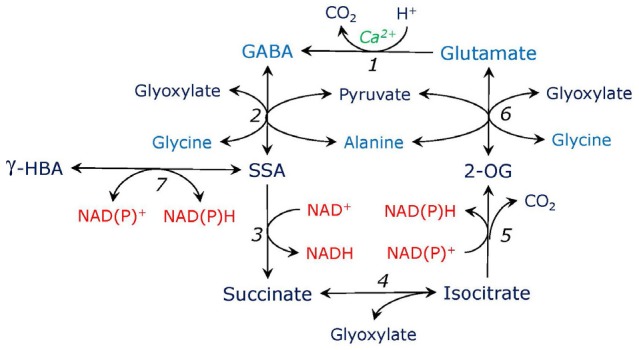
Putative γ-aminobutyrate-isocitrate cycle. Glutamate is decarboxylated by Ca-dependent glutamate decarboxylase (1), the reaction consumes proton and yields g-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA is transaminated to succinic semialdehyde (SSA) by aminotransferases using glyoxylate or pyruvate (2). SSA is oxidized to succinate by SSA dehydrogenase (3). Succinate in the reaction with glyoxylate forms isocitrate, the reaction is catalyzed by the cytosolic form of isocitrate lyase (4). The latter is oxidized to 2-oxogutarate (2-OG) by isocitrate dehydrogenase (5). 2-OG is transaminated to glutamate by aminotransferases using glycine or alanine (6), use of other amino donors such as serine or aspartate is also possible (not shown). SSA can be converted to γ-hydroxybutyrate (γ-HBA) by SSA reductase which is also glyoxylate reductase (7).
