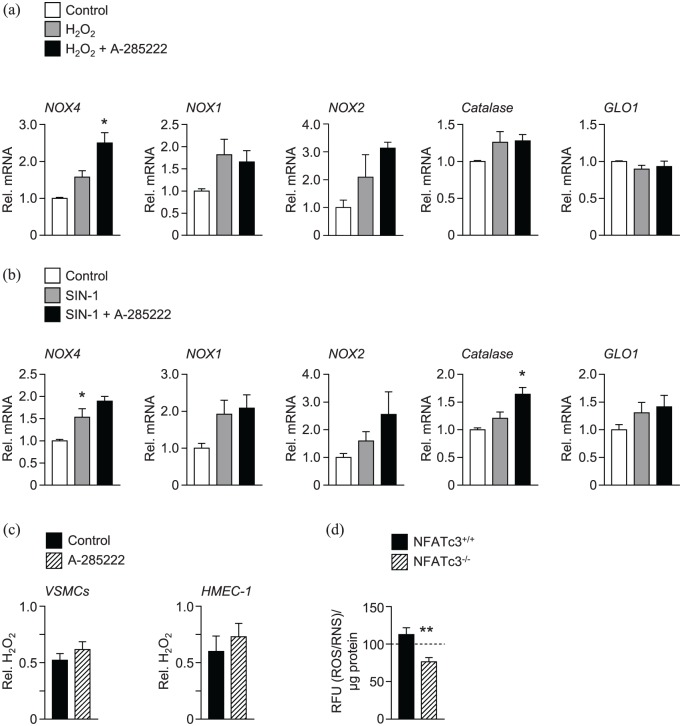
Figure 4.
In vitro inhibition of NFAT increased the expression of the anti-oxidant enzymes NOX4 and catalase in VSMCs. Mouse VMSCs were incubated with (a) H2O2 (500 µmol/L) or (b) SIN-1 (100 µmol/L) for 48 h in the presence or absence of A-285222 (1 µmol/L). The expression of oxidative stress targets NOX4, NOX1, NOX2, catalase and GLO1 was measured using qPCR and are expressed relative to untreated control cells. N = 4–7 experiments/condition *p < 0.05. (c) H2O2 levels were measured in the medium of VSMCs and HMEC-1 cells after 24 h in high glucose (25 mmol/L; HG) in the presence or absence of A-285222 (1 µmol/L). H2O2 levels were normalized to protein and expressed relative to control without A-285222 (N = 6–16 experiments/condition). (d) ROS/RNS levels, expressed as relative fluorescence units (RFU) were measured in the cell culture medium of VSMCs from NFATc3 competent (NFATc3+/+) and knockout (NFATc3–/–) mice in the presence of high glucose concentration (25 mmol/L) during 48 h. The dashed line shows ROS/RNS levels measured under low glucose conditions (5 mmol/L) as a reference (N = 9 experiments/condition).