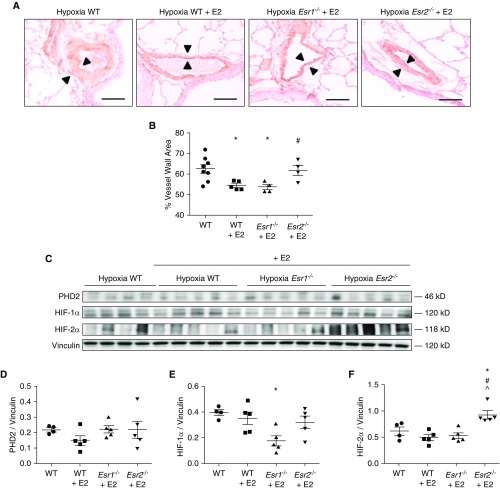
Figure 7.
ERβ is necessary for E2-mediated attenuation of hypoxic pulmonary vascular remodeling and HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression in mice. (A) Representative immunohistochemical images of lung sections stained for smooth muscle actin from untreated wild-type (WT) (solid circles), E2-treated WT (solid squares), E2-treated Esr1−/− (solid triangles), and E2-treated Esr2−/− (solid inverted triangles) mice exposed to chronic hypobaric hypoxia (Patm = 362 mm Hg; equivalent to 10% FiO2; 3 wk). Note the decrease in vascular wall thickness (arrowheads) in E2-treated WT and Esr1−/− mice, but not in E2-treated Esr2−/− mice compared to WT controls. Scale bars = 50 μm. (B) Quantification of the wall thickness of small- and medium-sized pulmonary arteries (less than 200 μM). (C) PHD2, HIF-2α, and HIF-1α protein expression in mouse lung homogenates from WT, E2-treated WT, E2-treated Esr1−/−, and E2-treated Esr2−/− mice exposed to chronic hypobaric hypoxia. (D–F) Expression levels of lung PHD2, HIF-2α, and HIF-1α quantified by densitometry; n = 4–5 per group. Scatterplots include means ± SEM. *P < 0.05 versus WT; #P < 0.05 versus WT + E2; ^P < 0.05 versus Esr1−/− (one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s test). E2 = 17β-estradiol.