FIGURE 1.
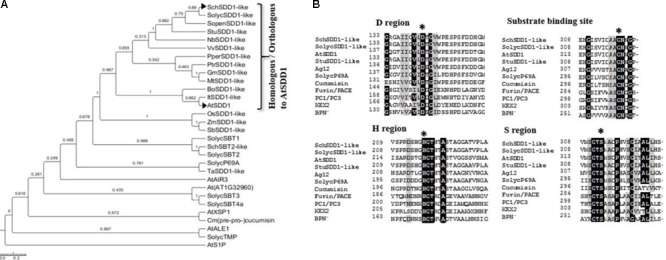
Phylogenetic relationships and sequence alignment of the deduced SchSDD1-like and other homologous subtilisin proteins. (A) Phylogenetic relationship between SchSDD1-like and other homologous SBT sequences. The multiple sequence alignments were performed by Clustal W 1.83 and the phylogenetic tree was constructed with Mega 6.0 using the NJ method. The GenBank, Solgenomics and Gramene accession numbers of the SBTs selected to draw the phylogenetic tree were described in the Section “Materials and Methods”. (B) Alignment of the sequences of the characteristic domains of various subtilisin-like serine proteases and SchDD1-like. These include the D, H, and S regions, which together form the catalytic triad, and the substrate binding site of different subtilisin-like serine proteases. SDD1 from A. thaliana (Berger and Altmann, 2000), Ag12 from A. glutinosa (Ribeiro et al., 1995), LeP69 from tomato (Meichtry et al., 1999), cucumisin from melon (Yamagata et al., 1994), FURIN/PACE (Wise et al., 1990) and PC1/PC3 from human (Smeekens and Steiner, 1990), KEX2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Mizuno et al., 1988) and subtilisin BPN’ from B. amyloliquefaciens (Wells et al., 1983) are shown. Three characteristic catalytic domains (D, H and S regions) and a substrate binding site (N) are marked with an asterisk. Identical residues (>75%) are highlighted in black while similar amino acids are highlighted in gray.
