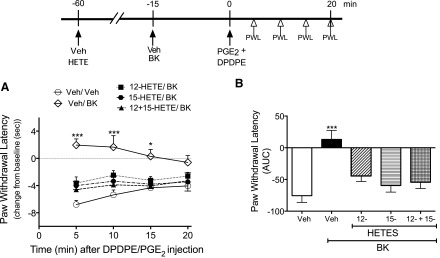
Fig. 5.
Pretreatment with the 12-/15-LOX–dependent AA metabolites 12-HETE and 15-HETE attenuates DPDPE-mediated anti-allodynia. Rats received intraplantar injections of vehicle (Veh), 12-HETE (0.1 µg), 15-HETE (0.1 µg), or 12-HETE and 15-HETE combined. After 45 minutes, rats were injected with Veh or BK (25 µg), and then 15 minutes later received coinjections of PGE2 (0.3 µg) with DPDPE (20 µg). (A) PWL was measured before (baseline) and at 5-minute intervals after the PGE2/DPDPE injection for 20 minutes. Data were evaluated for statistical differences with two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Tukey’s post hoc analysis. (B) Area under the individual time-course curves (AUC) for each pretreatment condition. Data were evaluated for statistical differences with one-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s post hoc analysis. Data represent mean ± S.E.M. of 6 (Veh-Veh pretreatment), 9 (Veh-BK pretreatment), 12 (12-HETE/BK pretreatment), 9 (15-HETE/BK pretreatment), or 4 (12- + 15-HETE/BK pretreatment) animals per group. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 compared with Veh/Veh/DPDPE + PGE2 (i.e., no pretreatment with BK). As shown in Supplemental Fig. 1 and 2, 12-HETE and 15-HETE did not alter either baseline PWL or PGE2 -evoked PWL.