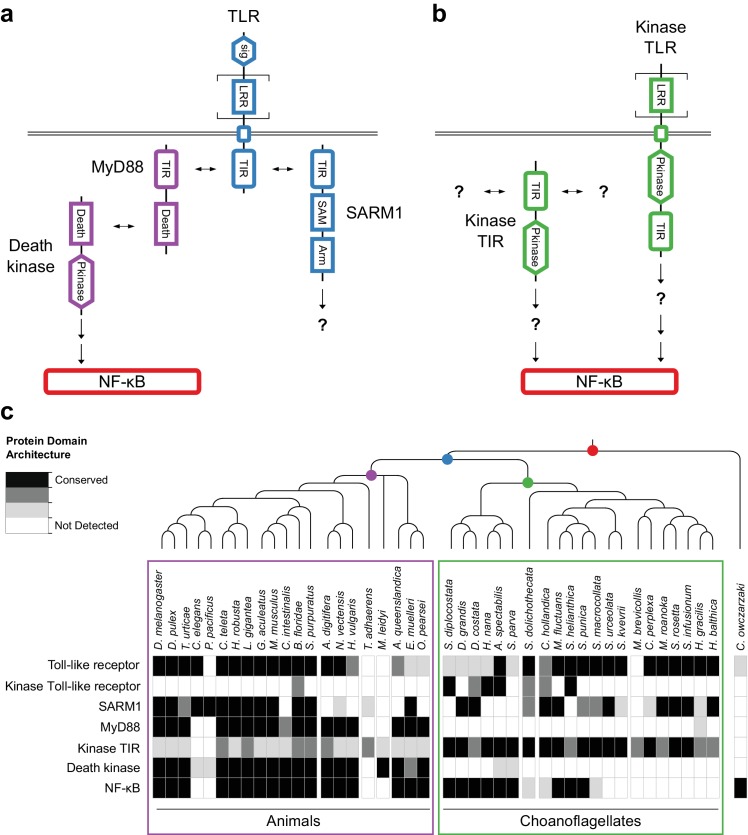
Figure 4. Evolution of the TLR signaling pathway.
Components of the canonical TLR pathway (a) and a potential choanoflagellate Kinase TLR signaling pathway (b), with their canonical domain architectures and colored by their inferred ancestral origin (blue = choanozoan ancestry, purple = metazoan ancestry, green = choanoflagellate ancestry, and red = holozoan ancestry). Question marks denote steps of the signaling pathway and/or interaction partners that are hypothesized, but untested. (c) Presence of receptors, adapters, kinases and the transcription factor NF-κB in animals, choanoflagellates and C. owczarzaki.