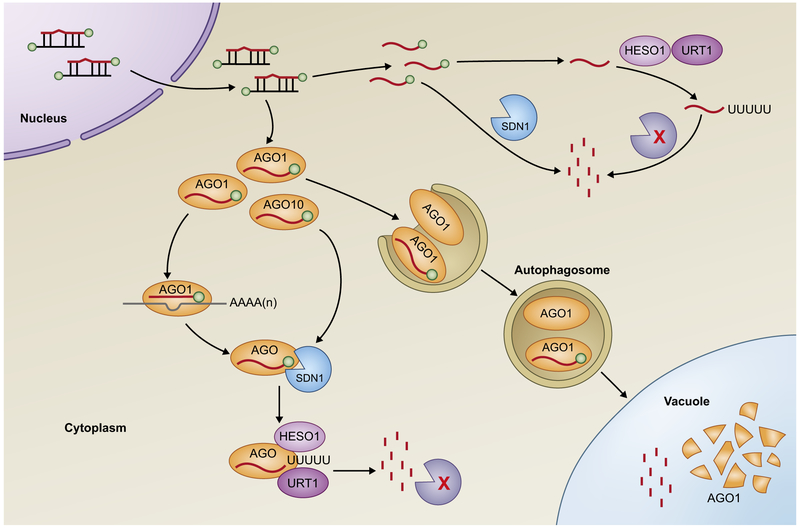
Fig. 3.
Mechanisms of plant microRNA (miRNA) turnover. miRNA degradation starts with the removal of the methyl group at the 3′ end by SMALL RNA DEGRADING NUCLEASE 1 (SDN1), which is followed by 3′ uridylation through HEN1 SUPPRESSOR 1 (HESO1) and/or UTP:RNA URIDYLYLTRANSFERASE 1 (URT1). The tailed miRNAs are subsequently degraded by an unknown exonuclease. SDN1 and nucleotidyl transferases (HESO1 and URT1) can act on both ARGONAUTE (AGO)-bound miRNAs and free miRNAs in the cytoplasm. Free miRNAs are also degraded by SDN1 directly. The degradation of AGO1 via autophagy may also contribute to miRNA turnover.