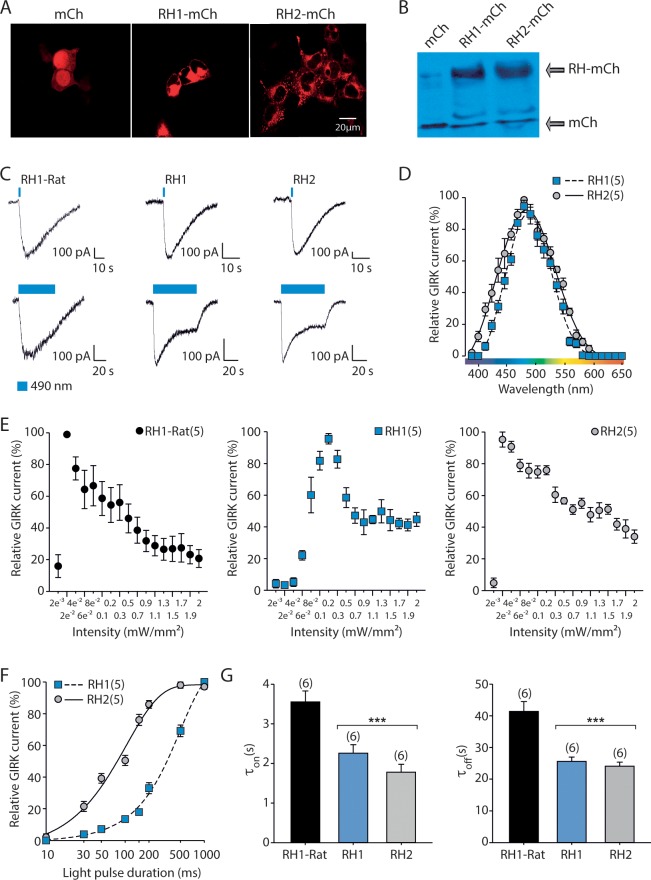
Fig 4. Characterization of the action spectrum and biophysical properties of Anomalops katoptron RH1 and RH2.
(A) Distribution of mCherry, RH1-mCherry and RH2-mCherry in tsa201 cells. (B) Western blot analysis of tsA201 homogenates expressing mCherry, RH1-mCherry and RH2-mCherry. Protein expression was detected with an antibody against mCherry. (C) Comparison of light-induced GIRK (G protein coupled inward rectifying potassium) currents activated by RH1-Rat, A. katoptron RH1 and A. katoptron RH2 using a 1 s or 10 s light pulse of 490 nm (indicated as blue bar). (D) Wavelength dependence of maximal GIRK current activation induced by RH1-Rat, A. katoptron RH1 and A. katoptron RH2 using a 1 s light pulse of the indicated pseudorandomized wavelength. (E) Light pulse intensity dependence of maximal GIRK current activation induced by RH1-Rat, A. katoptron RH1 and A. katoptron RH2 using a 1 s light pulse of 490 nm with different pseudorandomized light-intensities. (F) Light pulse duration dependence of maximal GIRK current activation induced by A. katoptron RH1 and A. katoptron RH2 using a light pulse of 490 nm with increasing time. (G) Activation and deactivation time constants of GIRK currents induced by RH1-Rat, A. katoptron Rh1 and A. katoptron RH2 using a light pulse of 470 nm for activation with increasing time. The number of cells analyzed is indicated in parentheses. Statistical significance was evaluated with ANOVA (***p<0.001).