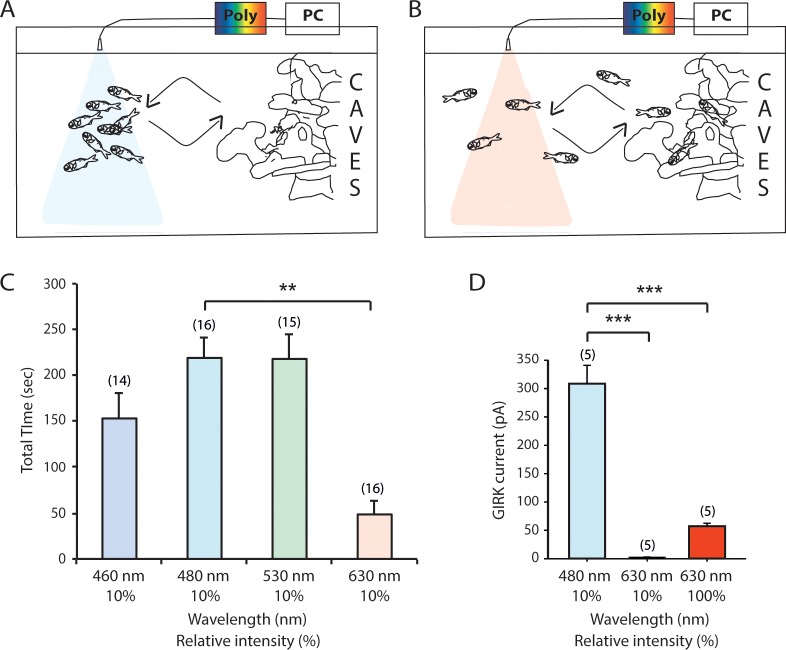
Fig 6. Characterization of the wavelength and intensity dependence on conditioned feeding behavior of Anomalops katoptron.
(A-B) Schematic representation of the behavioral food conditioning experiment (polychromatic light source, Poly). A school of 8 A. katoptron fish were trained to recognize food delivery associated with high intensity red light (100% at 630 nm, 2 mW/mm2, conditioned stimulus). (A) Low intensity blue light (10% at 480 nm) attracted the fish to the feeding area. (B) Low intensity red light (10% at 630 nm) did not attract the fish to the feeding area. (C) Characterization of the wavelength dependence on conditioned feeding behavior of A. katoptron. Wavelength dependent feeding behavior of A. katoptron was measured at 460 nm, 480 nm, 530 nm and 630 nm with 10% light intensities delivered by the polychromatic light source at a given wavelength. (D) Low intensity blue light (10% at 480 nm) but not low intensity red light (10% at 630 nm) activates RH1 mediated GIRK currents. However, high intensity red light (100% at 630 nm) induced RH1 mediated GIRK current, which is about >20% of the current induced by 480 nm (10% intensity). The total number of trials per data point is indicated in parentheses. Statistical significance was evaluated with ANOVA (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001).