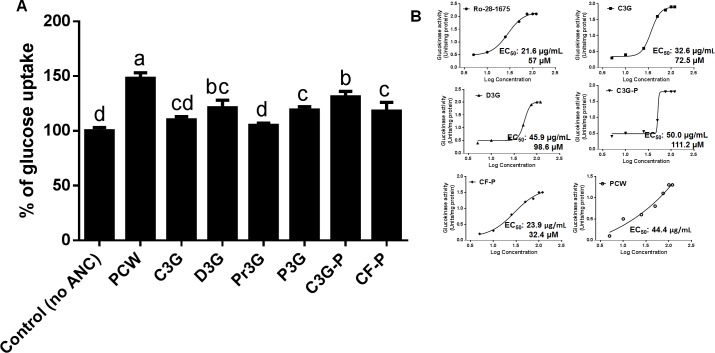
Fig 8. Effect of anthocyanins from purple corn on glucose uptake and GK-activating potential in HepG2 cells.
A) Effect of pure anthocyanins (ANC) and ANC-rich extracts from purple corn in glucose uptake in HepG2 cells. The cells were treated with 0.4 mg/mL of the ANC-rich extract from purple corn pericarp water extract (PCW), 50 μM of pure ANC cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (C3G), delphinidin-3-O-glucoside (D3G), pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside (Pr3G), peonidin-3-O-glucoside (P3G), the semipurified C3G from purple corn pericarp (C3GP) and catechin-(4,8)-cyanidin-3,5-diglucoside condensed form (CF). Results are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Bars with different letters means statistical difference (p < 0.05) as determined by Tukey’s test. B) GK activation by ANC from purple corn as determined using a biochemical assay. A non-linear regression was used to determine the half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) based on the method by Sebaugh [61]. The cells were treated with a glucokinase agonist Ro-28-1675 (1 μM– 100 μM), different concentrations of pure ANC (1 μM– 300 μM), and PCW (0.125 mg/mL– 0.5 mg/mL). The results are expressed as units of glucokinase activity per milligram of protein in the cell lysates (Units/mg protein) versus the log concentration of the samples.