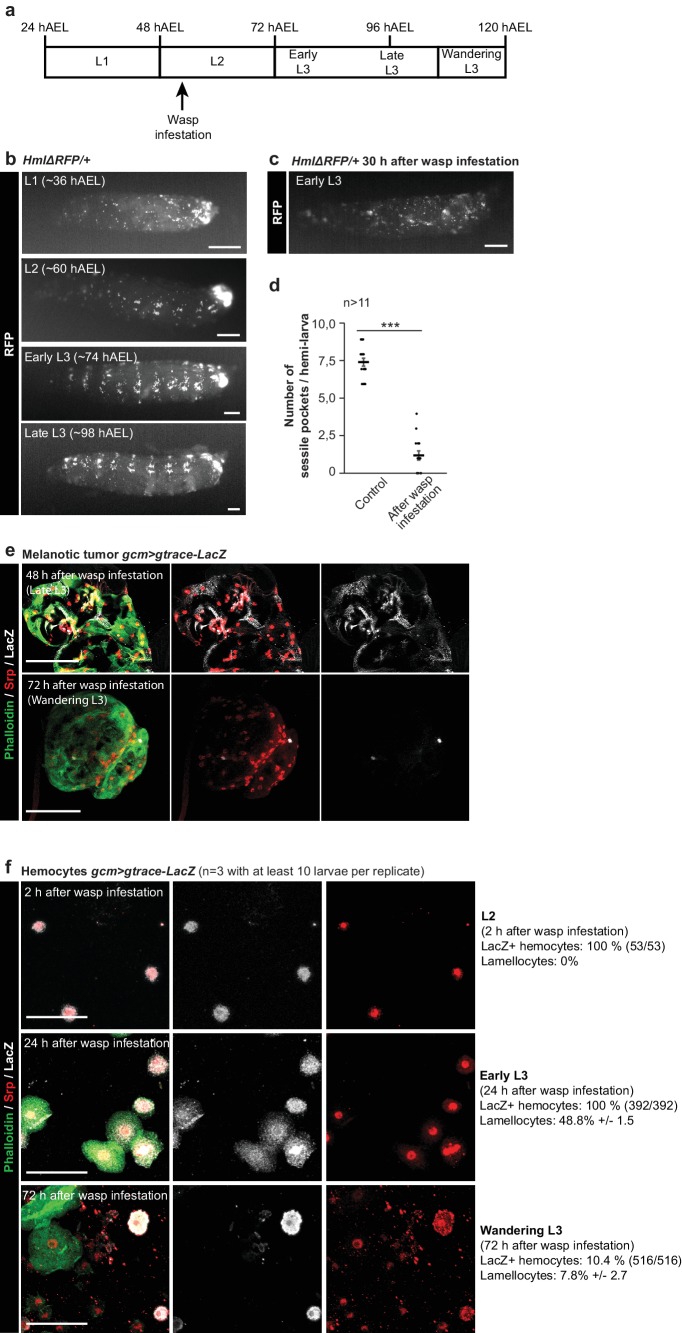
Figure 9. Impact of the wasp infestation on the hemocytes.
(a) Schematic of the correspondence between the timeline after egg laying (AEL) and the larval developmental stage. The wasp infestation was carried out at the L2 stage. (b–c) RFP signals from HmlΔRFP/+larvae at L1, L2, Early L3 and Late L3 stages (b) and Early L3 after wasp infestation (c). The HmlΔRFP transgene induces the expression of RFP in hemocytes starting from L1 (Makhijani et al., 2011). The larvae display an accumulation of hemocytes in the sessile pockets from the L2 stage onward. Upon wasp infestation, the sessile hemocytes are released into circulation. Scale bar: 200 µm. (d) Number of sessile pockets per Late L3 larva (one lateral view per larva = hemi larva) in normal conditions and after wasp infestation. Each hemi-larva is represented by a dot, the bar represents the average and the error-bars s.e.m., n > 11, p-value measured using student test after variance analysis. (e) Representative examples of melanotic tumors at different stages. Immunolabelling of tumors from gcm> gtrace LacZ larvae, 48 hr and 72 hr after wasp infestation. Phalloidin (green), Srp (red) and LacZ (white). Left panels show the merged channels, mid panels show LacZ and Srp labelling and the right panels show LacZ labelling alone. Scale bar: 100 µm. (f) Immunolabelling of gcm> gtrace LacZ larval hemocytes 2 hr, 24 hr and 72 hr after wasp infestation. Phalloidin (green), Srp (red) and LacZ (white). The left panels show the merged channels, the mid panels show LacZ labelling alone and the right panels show Srp labelling alone. Lamellocytes can be recognized by the strong expression of Phalloidin and by their very large size. Scale bar: 50 µm.