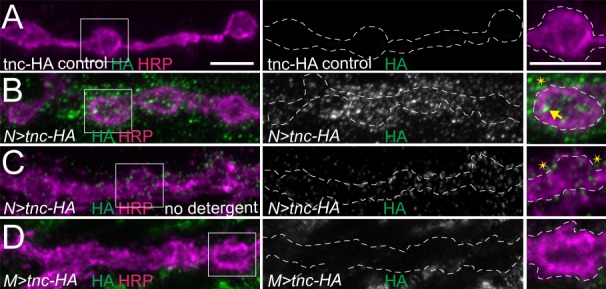
Figure 1. Tnc is expressed in neurons and muscles and concentrates at the synaptic cleft.
(A–B) Diagram of the tnc gene and the Tnc protein domains: vWFC (orange), Pro/Thr/Ser-rich, mucin specific domains (gray), and RGD motifs (red). The antigen for the anti-Tnc antibody is marked in green. (C–E) Western blot analyses of lysates from larval brains or muscles and transiently transfected S2 cells. Tnc can be detected in control but not in tnc mutants (C) and is reduced by knockdown of tnc in neurons or muscle (E). Tnc is efficiently secreted in the S2 cell media (S) compared with the cell pellet (P). (F–J) Confocal images of NMJ4 boutons of indicated genotypes stained for Tnc (green) and HRP (magenta). Low levels of Tnc surround synaptic boutons in control but not tnc mutant NMJs (F–G). Expression of Tnc in neurons but not in the muscles induces accumulation of Tnc-positive puncta in and around the NMJ boutons. The small puncta (asterisks) appear to be extracellular, as they are still present in detergent-free staining conditions (I), whereas the large aggregates (arrows) likely correspond to intracellular secretory compartments. Scale bars: 5 μm. Genotypes: tncEP(or 82)/Df (tncEP(or 82)/Df(3R)BSC655); N > tncRNAi (BG380-Gal4/+;UAS-tncRNAi/+); M > tncRNAi (UAS-tncRNAi/G14-Gal4); N > tnc (UAS-tnc/+; elav-Gal4/+); M > tnc (UAS-tnc/BG487-Gal4).
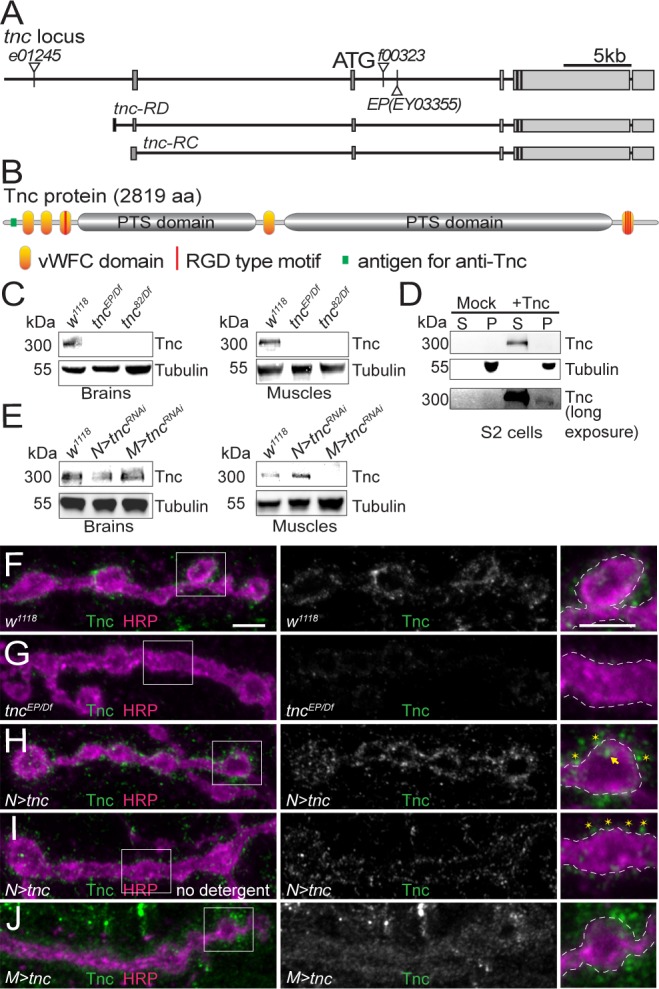
Figure 1—figure supplement 1. Tnc distribution in embryonic and larval tissues.
Figure 1—figure supplement 2. Addition of an HA tag does not change the distribution of overexpressed Tnc.