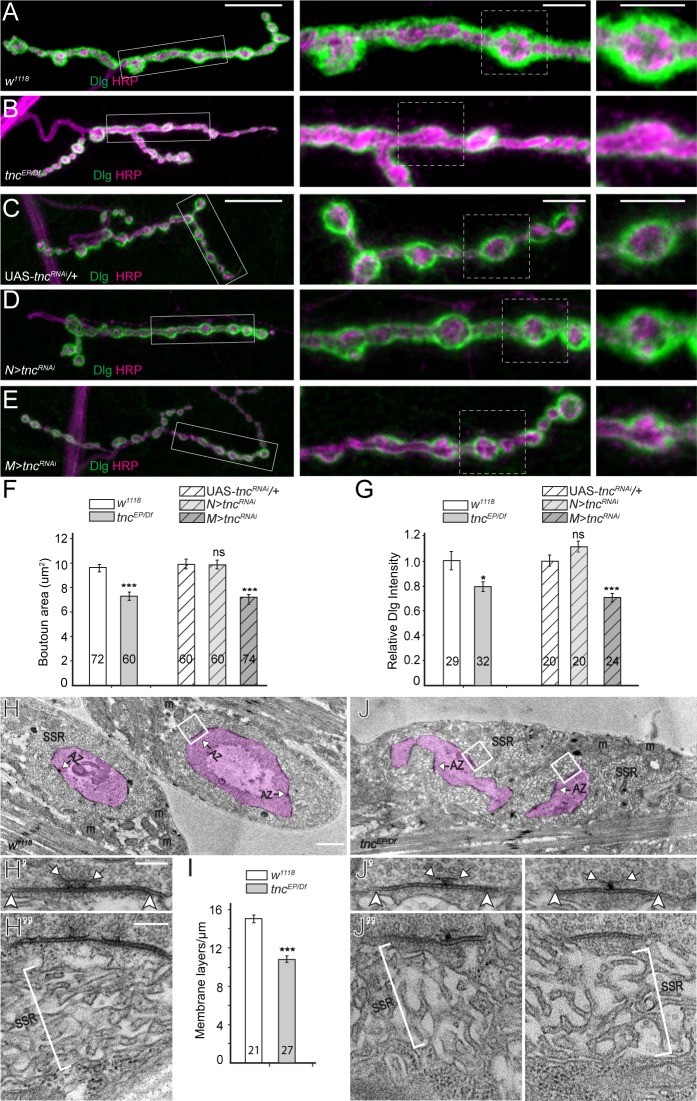
Figure 5. tnc mutants have smaller boutons and reduced SSR.
(A–E) Confocal images and analyses of third instar NMJ4 boutons of indicated genotypes stained for Dlg (green) and HRP (magenta). Compared to control, tnc mutant NMJs have smaller boutons and reduced perisynaptic Dlg levels (quantified in F–G). Knockdown of tnc in muscles but not in motor neurons recapitulates the mutant defects. (H–J) Electron micrographs of type Ib boutons. The neuronal compartment is labeled in magenta; the active zones (AZ, arrows), mitochondria (m), and subsynaptic reticulum (SSR, brackets) are indicated. The tnc mutants have sparse SSR with reduced density of the membrane layers (quantified in I). The tnc synapses appear normal (insert detail) but they reside in relatively distorted boutons. The number of samples examined is indicated in each bar. Bars indicate mean ±SEM. ns (p>0.05), *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. Scale bars: (A) 20 μm, 5 μm in boutons; (E) 2 μm, 200 nm in details. Genotypes: N > tncRNAi (BG380-Gal4/+; UAS-tncRNAi/+); M > tncRNAi (UAS-tncRNAi/+; 24B-Gal4/+)..