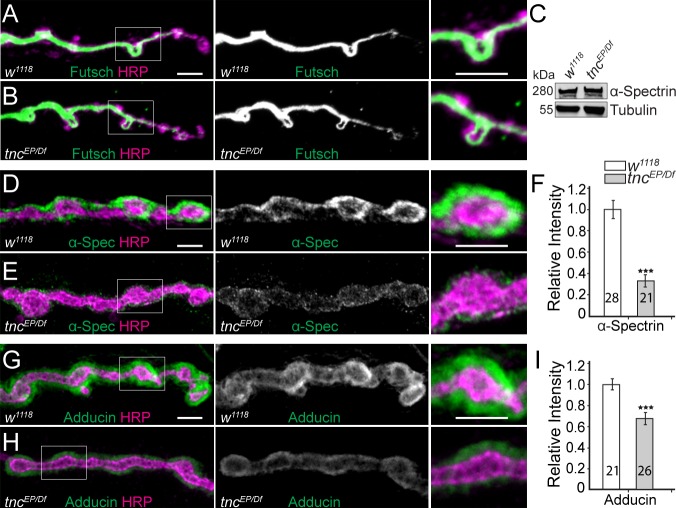
Figure 6. Diminished cortical skeleton at tnc mutant NMJs.
(A–B) Confocal images of NMJ4 boutons stained for Futsch (green) and HRP (magenta) reveal normal presynaptic Futsch-positive loops and microtubules bundles at tnc mutant NMJs. (C) Western blot analysis of lysates from larval carcasses show normal levels of α-Spectrin in tnc mutants. (D–I) Confocal images of NMJ4 boutons for the indicated genotypes stained for α-Spectrin (D–E), or Adducin (G–H) (green) and HRP (magenta), (quantified in F and I). α-Spectrin levels are dramatically decreased at tnc mutant NMJs; the reduction of Adducin is less drastic, but significant. The number of NMJs examined is indicated in each bar. Bars indicate mean ± SEM. ns (p>0.05), ***p<0.001. Scale bars: 5 μm.